10.4.2. Approval system description
The standard 'deliberate' procurement process is defined by six phases (with UK equivalents): Capabilities Assessment (Concept phase); Material Solution Analysis (Assessment phase); Technology Development; Integrated System Design (part of Demonstration phase); System Capability and Manufacturing Process Demonstration (part of Demonstration phase); and Production & Deployment (Manufacturing phase). An overview is given in Figure 10-2.
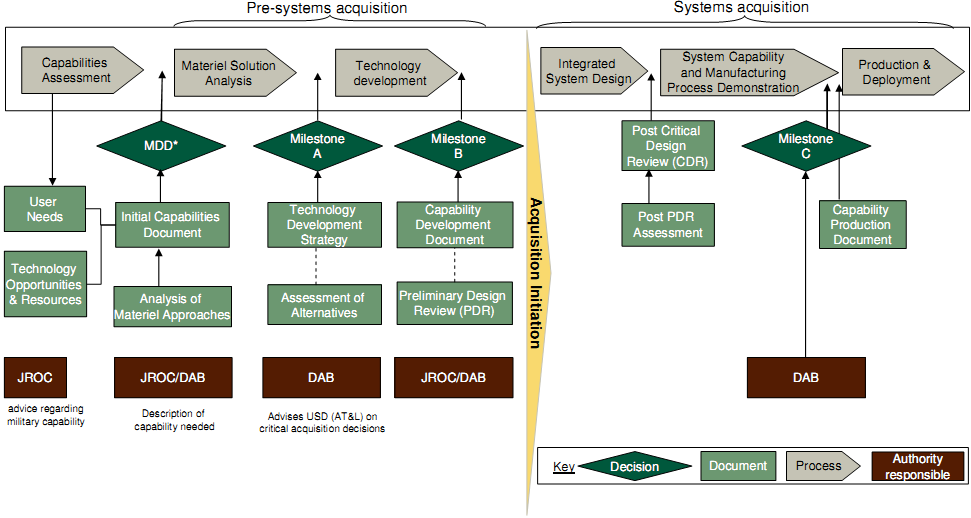
Source: DoD Instruction December 2008; GAO
Note: * Materiel Development Decision
Figure 10-2: Overview of the acquisition process in the US
The transition from each phase to the next is determined by a Materiel Development Decision review ("MDD"), milestone review, or design review. These reviews are based on the specific document produced during that phase, for example, the Initial Capabilities Document drafted for the MDD (broadly equivalent to business case at Initial Gate in the UK).
Projects are classified into four acquisition categories ("ACATs"), depending on the size of the development and procurement budgets, maximum single year expenditures, and special interests. The individual or body responsible for decisions (the Decision Authority) is dependent on the ACAT.
The DoD has established a preference for the use of evolutionary acquisition strategies relying on a spiral development process over 'big bang' acquisition124. Spiral development is defined as:
"an iterative process for developing a defined set of capabilities within one increment. This process provides the opportunity for interaction between the user, tester, and developer. In this process, the requirements are refined through experimentation and risk management, there is continuous feedback, and the user is provided the best possible capability within the increment. Each increment may include a number of spirals."125
Whereas in the UK, rapid acquisition is met through UORs delivered by DE&S, in the US there are seven organisations, some of which were established to meet specific needs, for example, that managed by the Joint Improvised Explosive Device Defeat Organization. The Lean Six Sigma project investigated what lessons from rapid acquisition can be applied to the 'deliberate' process in order to reduce cycle times. Evolutionary acquisition is the preferred DoD strategy for rapid acquisition of mature technology126.
One of the main differences with the UK is the practice of the Quadrennial Defense Review ("QDR"), which establishes the strategic direction for the DoD and reviews the organisational structures, processes and procedures to assess whether they will be effective in following this strategy. As stated in the 2006 preface, the QDR "is not a programmatic or budget document"127. The QDR directs the capability assessment decisions over the period.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
124 DoD Directive 5000.1, ‘The Defense Acquisition System’ (Oct 2000)
125 'Evolutionary Acquisition and Spiral Development', USD(AT&L) (Apr 2002)
126 DoD Instruction: Operation of the Defense Acquisition System 5000.02 (Dec 2008)
127 Quadrennial Defense Review Report 2006, DoD (Feb 2006)