4. United States PPP Financing or Delivery of Public-Use Infrastructure by Facility Type
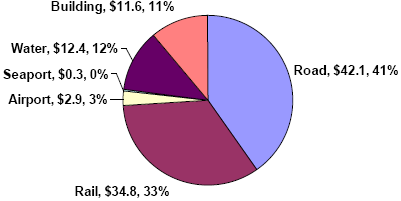
The total cost of PPP infrastructure projects in the United States planned or funded since 1985 has amounted to $104 billion, of which 40 percent has been for road projects, including highways, bridges, and tunnels (as shown in Figure 5). As with the worldwide statistics, road represents the largest category of PPP infrastructure projects in terms of costs. The second largest category of infrastructure project in terms of costs is rail, at 33 percent. Rail projects in the U.S. include light rail, commuter rail, mono-rail, high speed rail, and freight rail projects.
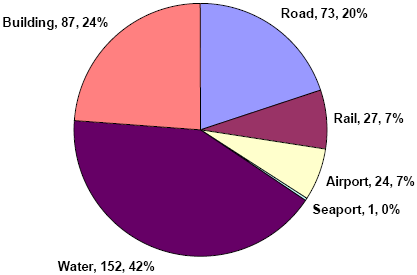
Water represents the largest category for the U.S. in terms of number of projects. However, water projects in the U.S. tend to be much less costly (average $82 million) than road projects (average $577 million).
Exhibit 5 -U.S. Infrastructure Projects Planned or Completed since 1985 by Project Type*
| Project Type | Total Planned & Funded Since 1985 | |||
| # | % | $ Billion | % | |
| Road | 73 | 20% | $42.1 | 40% |
| Rail | 27 | 7% | $34.8 | 33% |
| Airport | 24 | 7% | $2.9 | 3% |
| Seaport | 1 | 0% | $0.3 | 0% |
| Water | 152 | 42% | $12.4 | 12% |
| Building | 87 | 24% | $11.6 | 11% |
| Subtotal | 364 | 100% | $104.2 | 100% |
* Based on total PWF database, including projects with partial information
The distribution of PPP infrastructure projects by project type in the U.S. is illustrated in Exhibit 6, on the next page, in terms of number and cost of projects. These pie-charts illustrate the dominant infrastructure projects in the United States, in terms of total costs, are road and rail projects. However, more water and building projects are actually planned, although these tend to be much smaller than their road and rail counterparts which are much more capital intensive and time consuming to complete.
Exhibit 6 - Distribution of United States Infrastructure Projects Planned or Completed since 1985 by Project Type
| (Projects)
|
| ($ Billions)
|
* Based on total PWF database, including projects with partial information