Grantor accounting for service concession arrangements under IFRS - proposed approach under IFRIC 12
14. Once it has been determined that the PPP arrangement is a service concession within the meaning of IFRIC 12 the grantor should record the infrastructure as an asset. Normally, this would mean that the operator would not recognise any infrastructure asset because, from its viewpoint, the two conditions in paragraph 7 above (paragraph 5 of IFRIC 12) are met.
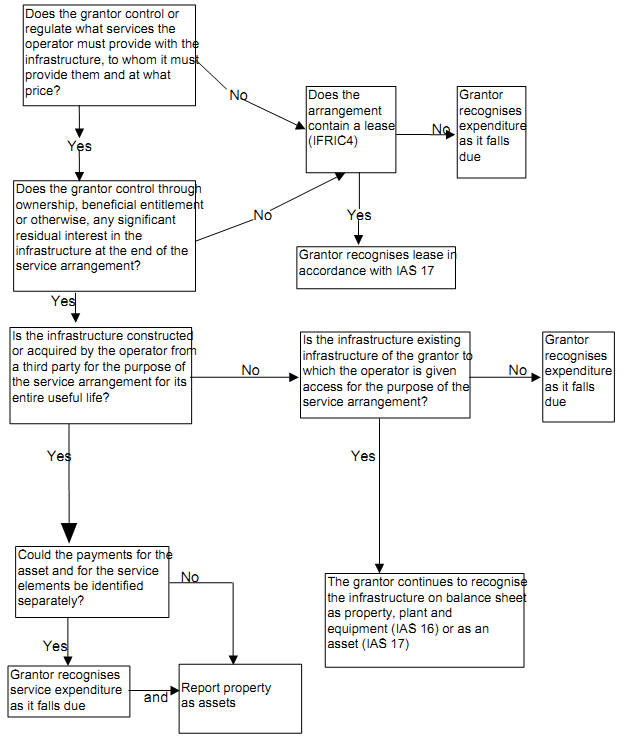
15. The flowchart overleaf provides a decision tree that helps the grantor to decide how to account for service concession arrangements under this approach.
16. In determining how to account for a PPP arrangement under IFRS, the grantor has first to determine whether it falls within the meaning of a service concession arrangement as set out in IFRIC 12. Once that decision has been taken, our preliminary view is that the next stage of the accounting analysis is to determine if the contract is separable between the service element and the infrastructure asset (see paragraphs 18 and 19). The grantor will also need to identify separately the interest charge included within the unitary payment.
17. Where an infrastructure asset is to be recognised by the grantor as a result of applying IFRIC 12, that asset should be valued in the same way as other assets of that generic type. The part of the contract relating to the services should be expensed because the service component of the transaction is not an asset; rather, it represents a recurrent obligation, which should be recognised as incurred over the term of the concession arrangement.