BENEFITS OF FDI FOR THE HOST COUNTRY
The attitude of most countries toward inward FDI has changed profoundly. Until the late 1970s, many countries, including most developing countries and those in the former Soviet bloc, were highly suspicious of foreign investment, often regarding it as a form of post-colonialism or dollar imperialism. Now almost all countries compete to attract foreign investment, recognizing the important benefits that inward FDI can bring to the host country.
Overall, foreign direct investment increases economic opportunities, employment and growth in host countries. In particular:
• It provides an increased pool of capital available for investment. Evidence suggests that, rather than replacing domestic investment, FDI supplements the capital shortfall and helps develop home capital markets by creating additional export possibilities.6
|
|
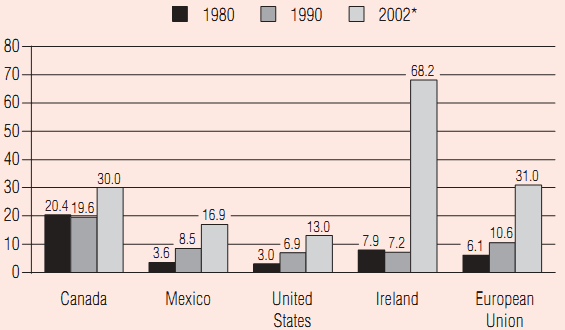
| * Year 2000 for Ireland and Mexico |
• It generates increased revenues for government, both directly through taxes paid by foreign investors and indirectly through additional employment income taxes and sales taxes generated by increased consumer spending.
• It leads to the acquisition of new and advanced technologies. Subsidiaries acquire these technologies and know-how from the global corporation. Other domestic firms that interact with these subsidiaries benefit from these transfers of technology and knowledge. Ultimately, FDI leads to higher productivity, improved quality of products and increased competitiveness:
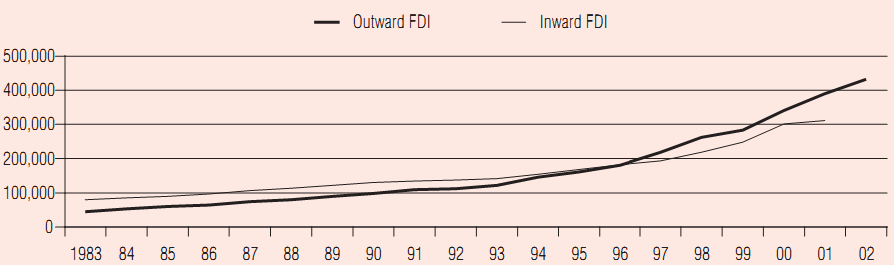
| Chart 4 Stocks of Canadian Outward FDI and Inward FDI ($ million) |
|
|
| Source: Department of Foreign Affairs and International Trade website <www.dfait-maeci.gc.ca>. Accessed May 11, 2004. |
- Foreign-controlled firms, on average, are 10 to 20 per cent more productive than domestically controlled firms, because of their superior technological and managerial know-how.7
- They also generate significant positive productivity "spillovers" to local firms. Linkages are often formed between multinational enterprises (MNEs) and local firms, creating additional employment, increased use of local materials and improved efficiency as a result of competition with the subsidiaries of MNEs.8
- These subsidiaries frequently export a substantial part of their production, earning additional foreign exchange.