Project Budget Variance
1.4 Approved budget variations are classified by DMO into three factors: price, exchange and real variations. The first two factors, price (material and labour) indexation and exchange rate variation are generally standard provisions in acquisition projects that extend over a number of years, and essentially represent budget variations outside the scope of project management to control.13 Across the nine 'repeat' projects from 2007-08, DMO data included in the PDSS indicates that all budget approval increases in 2008-09 were due to these factors.
1.5 Exchange rate variations in project budget are a result of projects' exposure to foreign currencies and movement in foreign exchange rates. Exchange rate variations impact projects where equipment is sourced from overseas, and can result in significant budget variations from one year to the next. For instance, in 2007-08 a stronger Australian dollar decreased the 15 projects' budget by a total of $1.5 billion. However, in 2008-09 the Australian dollar was weaker against most foreign currencies throughout the year and as a result, the budget for the 15 projects increased by a total of $3.4 billion due to exchange movements. In the second half of 2009, the Australian dollar has strengthened against most foreign currencies, and if this trend continues, then this would result in a decline in the foreign exchange component of project budgets in 2009-10.
1.6 Real variations in project budgets primarily reflect changes in the scope of projects, transfers between projects for approved equipment/capability, and budgetary adjustments such as administrative savings decisions. Across the nine repeat projects from 2007-08, there was only one budget variation related to scope change in 2008-09.14
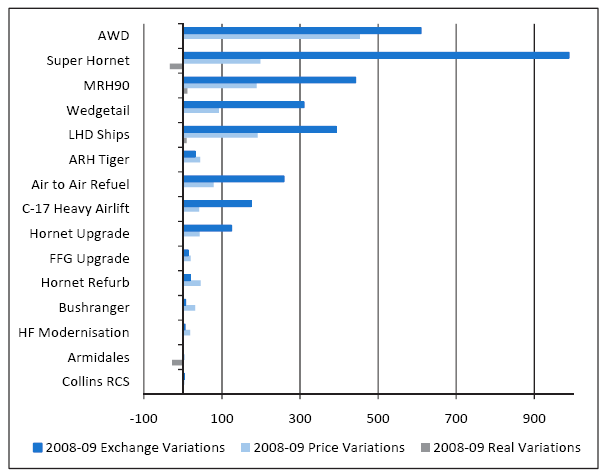
1.7 The in-year approved budget of the 15 projects from the 2008-09 Major Projects Report (MPR) increased by a total of $4.8 billion or 15 per cent. The increases mainly relate to price and exchange rate variations. As reflected in Figure 4, this budget increase was largely driven by the following projects:
• Super Hornet (24 per cent of the 15 projects' budget increase);
• AWD Ships (22 per cent of the 15 projects' budget increase);
• MRH90 (13 per cent of the 15 projects' budget increase); and
• LHD Ships (12 per cent of the 15 projects' budget increase).
Figure 4
In-Year (2008-09) Budget Changes ($m)
Sources: 2008-09 MPR and project budget approval history.
_________________________________________________________________________________
13 Australian Government arrangements for foreign exchange variation involve 'no win/no loss' supplementation. As a matter of policy, unless specifically approved, individual agencies cannot 'hedge' against foreign exchange risk.
14 This involved the Armidales transferring $27.8 million in approved funding from the project to the Defence Support Group to upgrade wharf facilities at Darwin and Cairns.