Project budgeted cost variance
2.7 Approved budgeted cost variations are classified by DMO into three main factors: price (material and labour) indexation, exchange rate variation and real variation. The first two factors, price indexation and exchange rate variation, are generally standard provisions in acquisition projects that extend over a number of years, and essentially represent budgeted cost variations that are outside the scope of project management to directly control.44
2.8 Real variations in project budgeted costs primarily reflect changes in the scope of projects, transfers between projects for approved equipment/capability, and budgetary adjustments such as administrative savings decisions.
2.9 In the case of the 22 projects in the 2009-10 MPR, all budgeted cost approval increases in 2009-10 were due to price indexation and exchange rate variations.
2.10 Of particular note in recent times is the impact of the exchange rate on projects' budgets. Exchange rate variations in project budgeted costs are a result of projects' exposure to foreign currencies and movement in foreign exchange rates. Throughout 2008-09, the Australian dollar was weaker against most foreign currencies. In the second half of 2009, the Australian dollar began strengthening against most foreign currencies, and reached a band around the US90 cents level for a considerable period of the 2009-10 financial year.
2.11 Figure 5 examines the three main factors contributing to budgeted cost variations in each of the last two years, and highlights the significant in-year impact of variations in the strength of the Australian dollar for the 22 projects in the 2009-10 MPR.
Figure 5
In-year (2008-09 and 2009-10) Budgeted Cost Changes ($m)
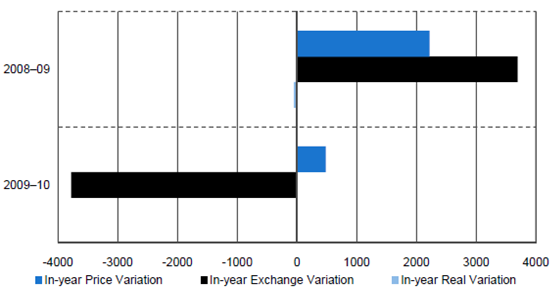
Source: 2009-10 MPR and Project Cost Approval Histories.
2.12 After a $3.7 billion (14 per cent) increase in project budgeted costs due to foreign exchange movements in 2008-09, the stronger Australian dollar in 2009-10 has led to a $3.8 billion (11 per cent) decrease in the budgeted cost of projects covered by the 2009-10 MPR (excluding other variations).
2.13 Overall, the 30 June 2010 approved budgeted cost of the 22 projects in the 2009-10 MPR decreased by $3.3 billion or 7.5 per cent, compared to their 30 June 2009 approved budget. The decrease was driven by foreign exchange variations, and offset slightly by a $0.5 billion increase due to price indexation. As reflected in Figure 6, projects that experienced a significant foreign exchange impact on their 2009-10 budgeted cost include:
● Next Gen Satellite ($248 million, or 22 per cent decrease in budgeted cost);
● Super Hornet ($720 million, or 17 per cent decrease in budgeted cost);
● MRH90 Helicopters ($504 million, or 12 per cent decrease in budgeted cost);
● LHD Ships ($438 million, or 12 per cent decrease in budgeted cost); and
● Air to Air Refuel ($220 million, or 11 per cent decrease in budgeted cost).
Figure 6
In-year (2009-10) Budgeted Cost Changes (percentage variation by factor)
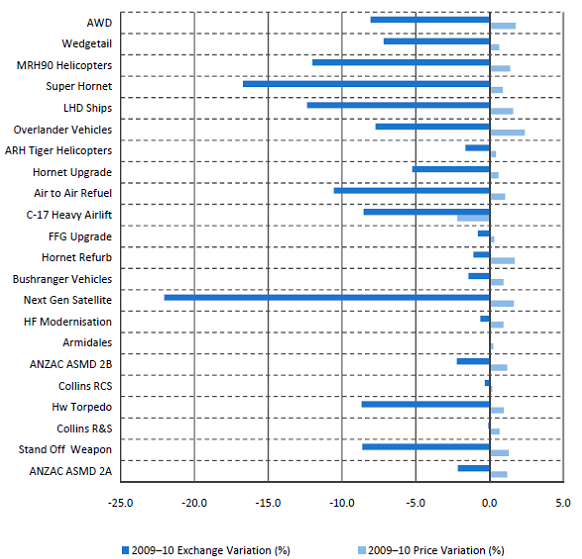
Sources: 2009-10 MPR and Project Cost Approval Histories.
________________________________________________________________________
44 Australian Government arrangements for foreign exchange variation involve 'no win/no loss' supplementation. As a matter of policy, unless specifically approved, individual agencies are not permitted to 'hedge' against foreign exchange risk.