Turnkey
| Turnkey is a traditional public sector procurement model for infrastructure facilities. Generally, a private contractor is selected through a bidding process. The private contractor designs and builds a facility for a fixed fee, rate or total cost, which is one of the key criteria in selecting the winning bid. The contractor assumes risks involved in the design and construction phases. The scale of investment by the private sector is generally low and for a short-term. Typically, in this type of arrangement there is no strong incentive for early completion of a project. This type of private sector participation is also known as Design-Build. Figure 5 shows the typical structure of a turnkey contract. | Basic features |
|
|
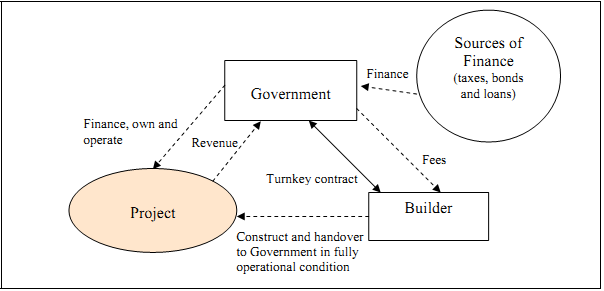
Figure 5. Turnkey contract
The main pros and cons of this model include the following:
| Pros: • Well understood traditional model • Contract agreement is not complex • Generally contract enforcement is not a major issue | Pros and cons of turnkey |
|
|
Cons:
• The private sector has no strong incentive for early completion
• All risks except those in the construction and installation phases are borne by the public sector
• Low private investment for a limited period
• Only limited innovation may be possible