Providers of finance
| The main providers of finance for the PPP project are: • Equity investment from project promoters and individual investors | Where the money comes from? |
|
| |
| • National and foreign commercial banks and financial institutions • Institutional investors • Capital market • International financial institutions |
Loans provided by national and foreign commercial banks and other financial institutions generally form the major part of the debt capital for infrastructure projects. The rate of interest could be either fixed or floating and normally loans are provided for a term shorter than the project period. Often two or more banks and financial institutions participate in making a loan to a borrower known as syndicated loan. Refinancing of the loan is required when the loans are provided for a maturity period shorter than the project period.
| The capital market can be a major source of funding. Funds may be raised as both equity and debt from the capital market by placement of shares, bonds and other negotiable instruments on a recognized domestic or foreign stock exchange. Generally, the public offering of these instruments requires regulatory approval and compliance with requirements of the concerned stack exchange. For example, companies must have three profitable years of operation before they can be listed on the Shenzhen and Shanghai exchanges. Securitization of existing assets is another relatively new mechanism in Asia which has been undertaken in China. Securitization is undertaken once the project is operating, after certain project risks such as construction delays, cost overruns and other initial risks have been mitigated. | Funding from capital market |
|
|
Institutional investors such as investment funds, insurance companies, mutual funds, pension funds normally have large sums available for long-term investment and may represent an important source of funding for infrastructure projects. Generally the institutional investors provide loans as subordinated debt.
International and regional financial institutions such as the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, the European Investment Bank, the Agence Francaise de Development and Islamic Development Bank can provide loans, guarantees or equity to privately financed infrastructure projects.
| When investors and financiers consider financing a project, they carry out extensive due diligence works in technical, financial, legal and other aspects of the PPP deal.31 This due diligence is intended to ensure that the project company’s (or SPV’s) business plan is robust and the company has the capacity to deliver on the PPP contract. | Due diligence |
The financing arrangement for a large project can be quite complex. For such a project the required finance normally comes from a large number of providers as can be seen from an example in figure 9.
FINANCING ARRANGEMENT FOR A 1070 MW HYDRO ELECTRIC POWER PROJECT IN LAO PEOPLE’S DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC
| Basic Information: | Total cost $1.25 billion; Debt-equity ratio: 72:28 |
| Financing: | 50% in Thai Baht and 50% in US Dollar |
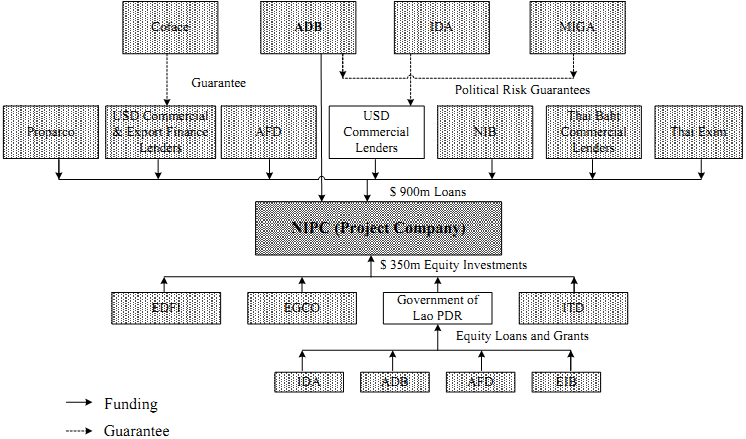
Notes: ADB = Asian Development Bank; AFD = Agence Française de Développement; Coface = Compagnie Française d’Assurance pour le Commerce Extérieur; EDFI = European Development Finance Institutions; EGCO = Electricity Generating Public Company Ltd.; EIB = European Investment Bank; IDA = International Development Association; ITD = Italian-Thai Development PCL.; MIGA = Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency; NIB = Nordic Investment Bank; Proparco = Société de Promotion et de Participation pour la Coopération Economique.
Figure 9. Financing arrangement for a large project
| Source: | Presentation made by the Asian Development Bank at a seminar organized by the Asian Development Bank Institute on 19-22 November 2007, Tokyo, Japan, and information from other sources. |
___________________________________________________________________________
31 Often the term “bankability” is used in the industry to refer to feasibility of a PPP project. The term, however, may mean different things to different parties in a PPP. But generally it may mean if the project is financial viable (from financial perspective), legally tenable (from legal perspective), and administratively implementable.