IV. THE CURRENT PPI PROGRAMME
Thirty-four types of projects are eligible under the PPI Act. These are grouped under 10 broad categories of roads, railways, harbours, culture and tourism, water resources, energy, environment, distribution, airports and communications. If a project falls into any of these 10 categories, it can be evaluated as a PPI project. The method of implementation must then be decided. The procedure for processing a solicited project has been simplified as shown in figure 2. The process has been modified to encourage competitive bidding for projects that are financially attractive. It also allows for negotiation of the terms of the concession agreement.
The Ministry of Planning and Budget, the concerned authorities and PICKO are involved in the selection of investment projects, evaluation of proposals and negotiation of concession agreements. The concerned authority (for example, the Ministry of Construction and Transportation in the case of transport projects) undertakes the initial activities for project development. The concerned authority is also responsible for approval of the engineering plan and confirmation of project completion.
The process for unsolicited project implementation is shown in figure 3. The procedure is similar to that for solicited projects but it also allows proposals from third parties. The private sector sponsor of a project prepares the project proposal and requests PICKO to review it. The project proposal is then evaluated by PICKO. If approved, a public notification of the proposal and its content is made and alternative proposals for the project from third parties are invited. A minimum of 60 days is allowed for submission of proposals by third parties. The proposals from third parties along with the initial proposal are evaluated and a winning bidder is selected. The initial proposer is given a bonus in the evaluation up to a maximum of 10 per cent of the total evaluation score. The project structure is determined through negotiations with the winning bidder.
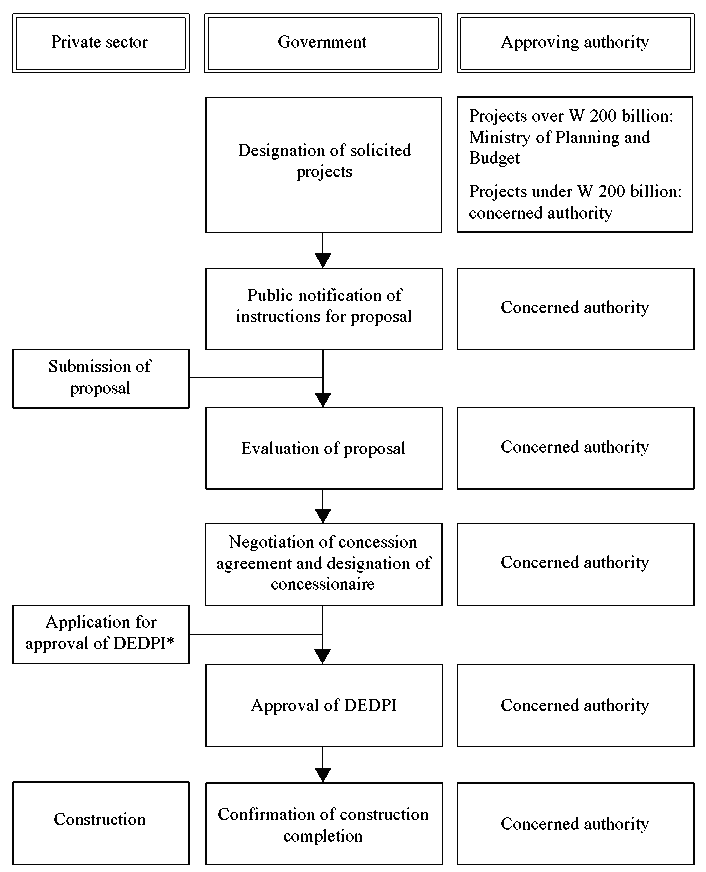
Source: PICKO, PPI Program and Investment Projects in Korea, (KRIHS, 2002).
* Detailed engineering design and plan for implementation.
Figure 2. Process for solicited project implementation
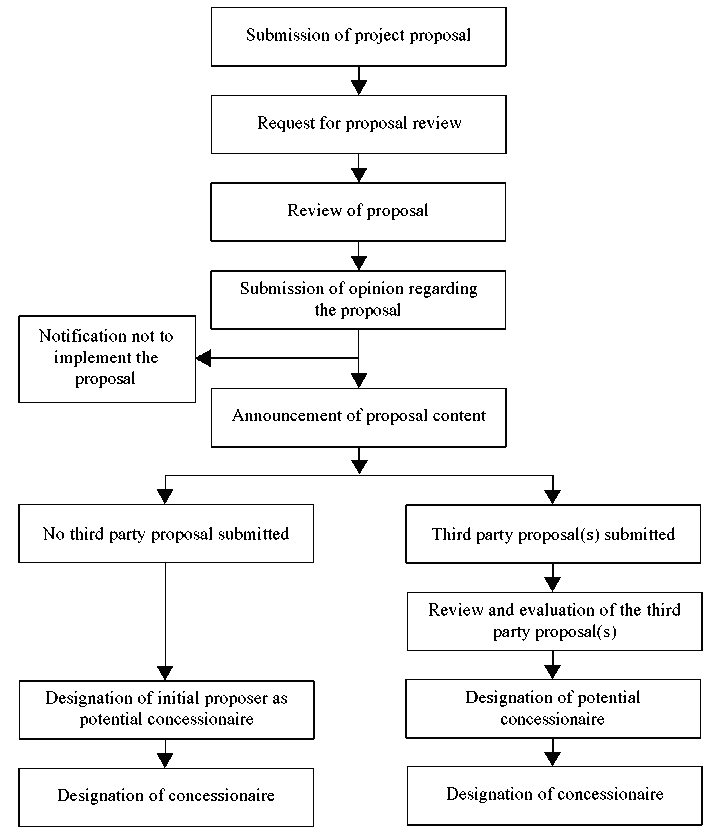
Source: PICKO, PPI Program and Investment Projects in Korea, (KRIHS, 2002), p. 16.
Figure 3. Process for unsolicited project implementation