ROAD-RELATED PPP ACTIVITY AROUND THE WORLD SINCE 1985
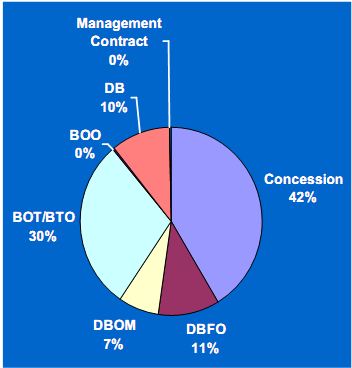
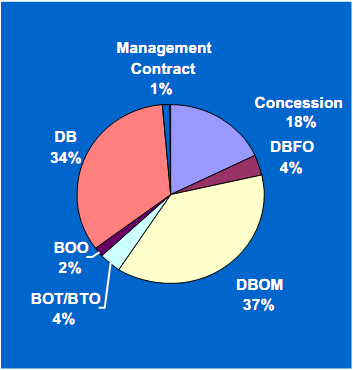
In comparison to the U.S., the use of PPPs between 1985 and 2004 has been more widespread overseas where concessions and BOT/BTO are the most widely used PPP approaches used, as shown in Exhibit 2.2 below. In addition, international spending on road-related PPP projects has been over six times the amount spent of these types of projects in the U.S. This reflects the greater level of responsibility and risk taken by the private partners involved in PPPs overseas, where the need for private capital financing is greater than in the United States which has traditionally relied on funding provided by motor fuel taxes paid into a trust fund intended solely for surface transportation capital and renewal projects.
Exhibit 2.2 Global Road-Related PPP Projects by Contract Type - 1985-2004
Global Excluding U.S. - $281B
| U.S. Only - $42B
|
Source: AECOM Consult, Inc. "Synthesis of Public-Private Partnership projects for Roads, Bridges & Tunnels from Around the World - 1985-2004", prepared at the request of the Federal Highway Administration, August 30, 2005, pp. 18 and 34. | |
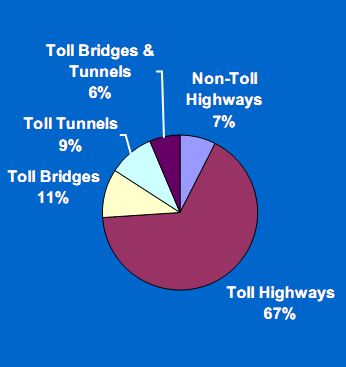
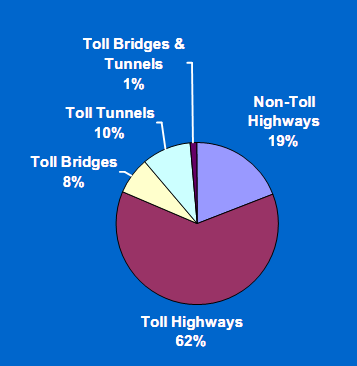
Exhibit 2.3 shows that, on average, the international community spent over two-thirds of its budget for road-related PPPs on toll highways between 1985 and 2004, with toll bridges the next largest category. In the U.S., the highest proportion of spending on road-related PPPs was also for toll highways, with non-toll highways the next largest facility type developed by PPPs during the same twenty-year timeframe. This reflects the importance of having a dedicated funding source such as tolls to support PPP projects regardless of sponsoring country.
Over the last 20 years, Europe has had the largest PPP infrastructure program in terms of road and rail project costs. Asia has had the second largest road and rail programs, although in recent years Asian countries have added significantly to their highway PPP projects. North America (Canada, Mexico, and the United States) have been third in terms of the cost of road and rail projects financed or delivered through some form of PPP arrangement. This may change as more project sponsors seek to leverage and expedite their capital improvement programs through the use of PPPs, innovative financing, and innovative project delivery.
Exhibit 2.3 Global Road-Related PPP Projects by Facility Type - 1985-2004
Global Excluding U.S. - $281B
| U.S. Only - $42B
|
Source: AECOM Consult, Inc. "Synthesis of Public-Private Partnership projects for Roads, Bridges & Tunnels from Around the World - 1985-2004", prepared at the request of the Federal highway Administration, August 30, 2005, pp. 17 and 33. | |