Whether PPP or Traditional Public Sector Financing is Preferable Depends on Project Specifics
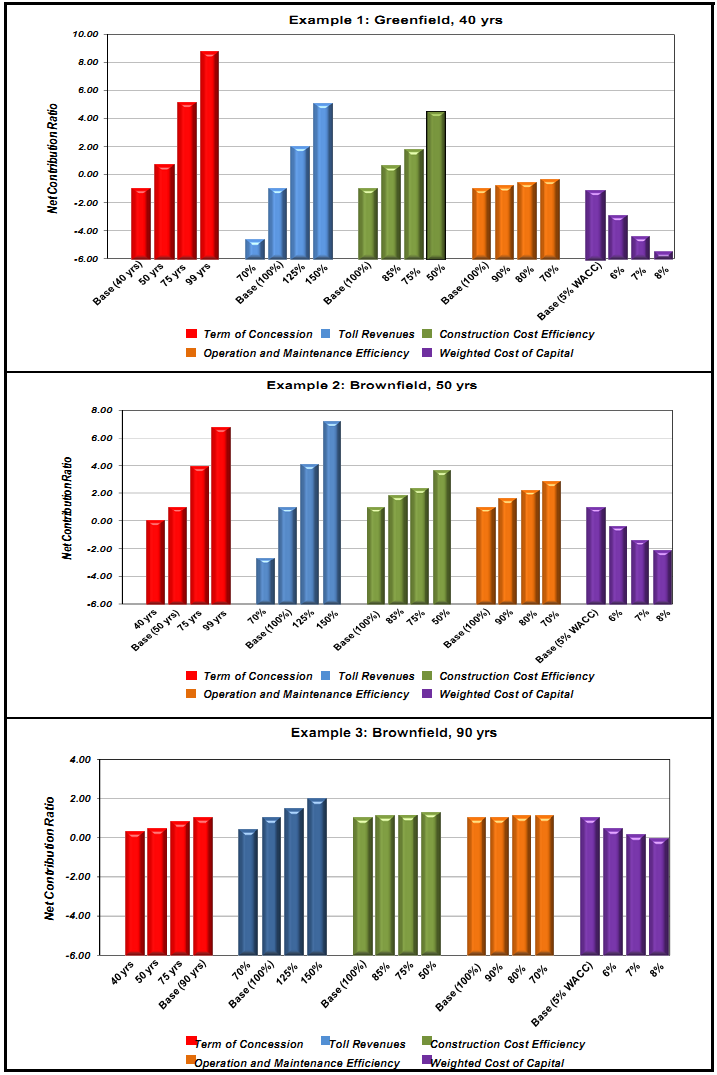
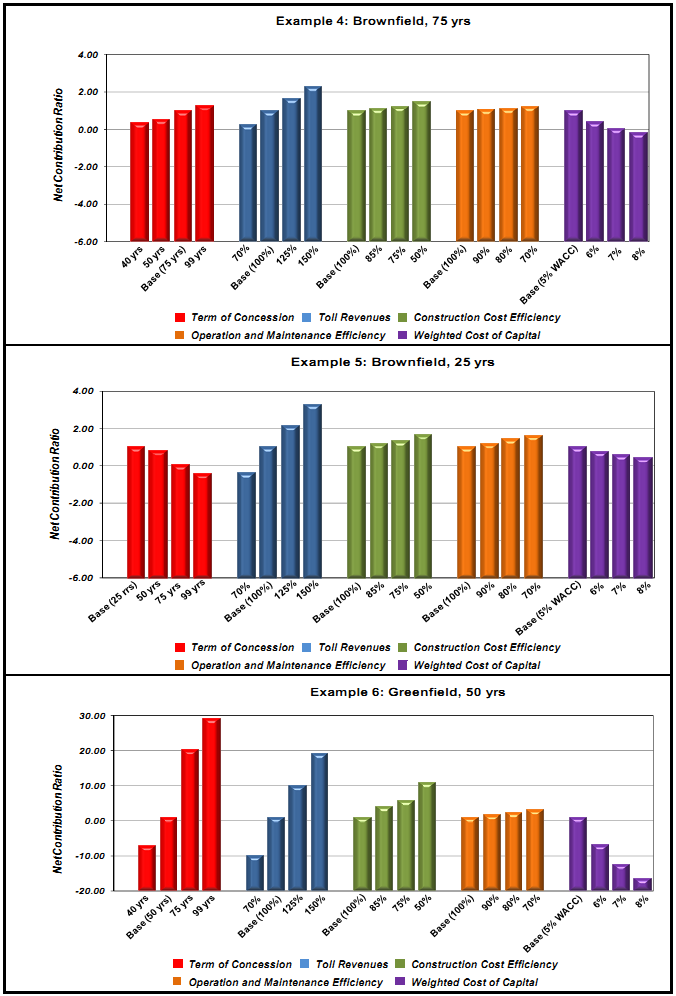
Generalizations about which financing approach is more advantageous to the public sector cannot be made because project specifics determine which approach is preferable.11 The impact of input variables on net contribution ratios for PPP transactions in our examples illustrates this point. Figure 7 on the following pages shows the results of sensitivity analyses with respect to key input variables: concession term; toll revenues; construction cost efficiency; O&M efficiency; and, cost of capital.12 We varied each factor and then measured the effect on the net contribution ratio. Large changes in the magnitude of the Figure's bars indicate large effects from changes in the input variables' values.
Figure 7 also illustrates the following points about PPPs and traditional financing:
• Each set of variables and each variable's impact magnitudes differ according to project;
• Private sector efficiencies with respect to facility O&M costs are not important value drivers, and, except in Project Example 2, construction cost efficiencies are not primary value drivers for brownfield projects;
• Toll revenues and concession terms are important value drivers for both greenfield and brownfield projects, but concession terms are significantly less important for brownfield projects;
• Cost of capital is a primary value driver in all our examples, except Project Example 5, in which the short contract term reduces its impact, and is especially important in greenfield projects.
• Brownfield projects are less sensitive to changes in variables than greenfield projects, substantiating the fact that greenfield projects contain greater operational, capital and financial risks.
Figure 7. Sensitivity of Input Variables
_________________________________________________________________________________________
11 The National Surface Transportation Infrastructure Financing Commission came to a similar conclusion: "[T]here is no overarching guide to the appropriateness of private sector financial participation. Each project's specific circumstance will determine the suitability of private sector involvement." Paying Our Way: A New Framework for Transportation Finance, Report of the National Surface Transportation Infrastructure Financing Commission, Washington, D.C., February 26, 2009, p. 177.
12 The differences between the public sector base cases and the PPP alternatives in this figure results from the assumption that the PPPs face a total tax rate of 35 percent. The cost of capital is assumed to not differ.