Decision Makers Can Use Our Analysis to Assist in Their Selections of Financing Methods
The determination of which financing method, a PPP or traditional financing, best meets a project's needs can be translated into a flowchart, which we developed for decision makers, as depicted in Figures 8 and 9. The first point of comparison, shown in Figure 8, concerns whether or not a project involves new construction. If so, the decision maker must determine whether or not a PPP will provide construction efficiencies. If construction efficiencies exist, then the question becomes whether or not they are large enough to make the PPP more attractive than the public alternative. If they are of sufficient scale, then the PPP is the preferable solution. However, if they are not large enough to overcome the inherent advantages of the traditional option, then the PPP's construction efficiencies and any efficiencies in revenue generation should be considered, since the combined efficiencies may make the PPP the better choice.
Figure 8. PPP vs. Traditional Financing: New Construction
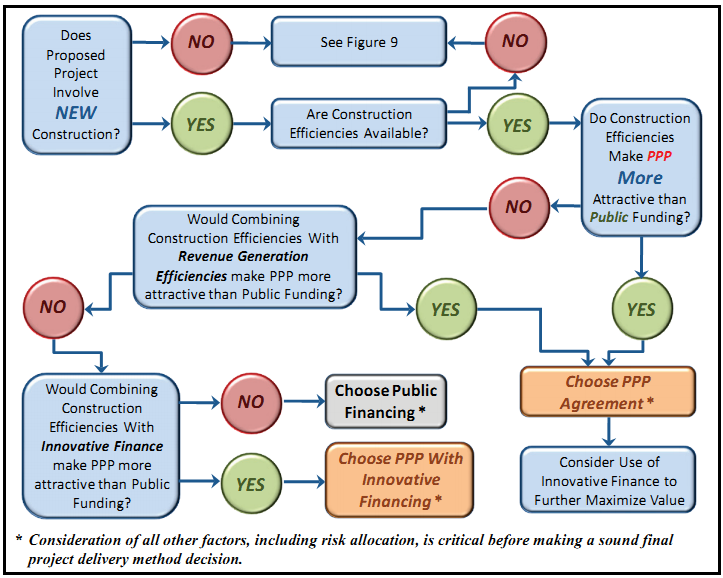
Source: OIG analysis
If the combination of construction and revenue efficiencies does not outweigh the public option's advantages, then the addition of innovative financing could make the PPP more attractive. If the combination of efficiencies and innovative financing cannot achieve the value that the traditional public financing alternative can, then public financing provides the more cost advantageous approach.
If no efficiencies in construction are available, then the question becomes whether efficiencies in revenue generation can be found under a PPP. Figure 9 illustrates the decision making process in this situation. If existing efficiencies are sufficient to make the PPP option more attractive than the public sector alternative, the PPP should be chosen. When efficiencies in revenue generation are present but are not of sufficient size to make the PPP a better value, then the addition of innovative financing should be considered. If the combination cannot overcome the traditional option's value, then public financing is the best choice.
Figure 9. PPP vs. Traditional Financing: Revenue Efficiencies
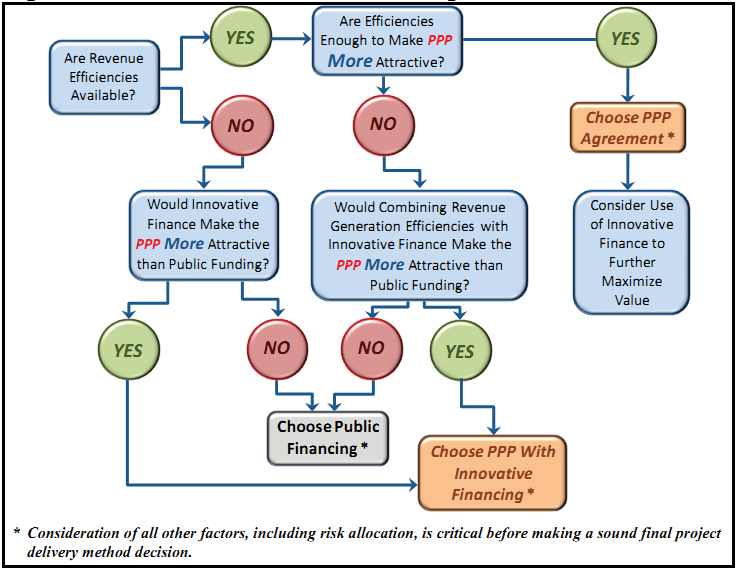
Source: OIG analysis
It is important to emphasize that decision makers should always consider various innovative financing tools when implementing a PPP arrangement. These tools may further enhance a PPP's value through reductions in the cost of capital.
Our analysis is purely financial, and the preceding flowcharts illustrate that financial analysis. A determination of whether to use a PPP or public financing ultimately needs to incorporate a broader range of factors than we considered in our analyses. Principal among these additional factors are different risk allocations and the possibility of more expedient project delivery. These factors can significantly affect a project's ultimate value.