GLOBAL USE OF PPPs TO ADVANCE ROAD-RELATED PROJECTS
Major changes in the economic strength and relationships among nations have prompted many of them to seek alternative ways to expedite the development of transportation infrastructure to improve regional accessibility and support their economic growth. Examples of this include:
• Creation of the European Union;
• Breakup of the Soviet Union;
• Reunification of eastern European nations with their western counterparts; and
• Emergence of both China and India as major players in the global economy.
The evolution of PPPs to rapidly meet these emerging needs has led to their refinement and proliferation in type and number, with many more countries moving to establish the legal authority to enter into PPPs to expedite financing and delivery of surface transportation projects prompted by the changes noted above.
The use of public-private partnerships to develop transportation infrastructure is more widespread in other parts of the world than in the United States. Exhibit 42 shows the dollar value of road, bridge, and tunnel projects funded and/or delivered as PPPs between the years 1985 and 2004 for each major region of the world, including PPP projects in the U.S. as part of the North America region.
Exhibit 42 - Number and Value of Road-Related PPPs by Global Region19
Region | Total Planned & Funded Since 1985 | Total Funded & Completed by 10/04 | ||||||
| # | % | $Billion | % | # | % | $Billion | % |
Africa | 14 | 2% | $4.8 | 1% | 7 | 2% | $3.7 | 2% |
Asia | 137 | 21% | $83.9 | 26% | 72 | 20% | $44.5 | 28% |
Europe | 205 | 31% | $139.1 | 43% | 91 | 25% | $58.1 | 37% |
Latin America | 126 | 19% | $26.2 | 8% | 83 | 23% | $18.9 | 12% |
North America | 174 | 27% | $70.8 | 22% | 106 | 30% | $32.2 | 20% |
Total | 656 | 100% | $324.7 | 100% | 359 | 100% | $157.3 | 100% |
As revealed by Exhibit 42, Europe has been the leader in using PPP approaches to delivery road-related infrastructure projects. Even with the U.S. transportation PPP projects included in the totals for North America in this chart, North America has lagged behind both Europe and the Asian continent in terms of budgeted PPP projects. However the North America region has the second largest number of PPP projects planned and funded, and the largest number funded and completed from 1985 to 2004. However, these larger numbers are indicative of much smaller PPP projects, including maintenance management contracts and smaller design-build contracts.
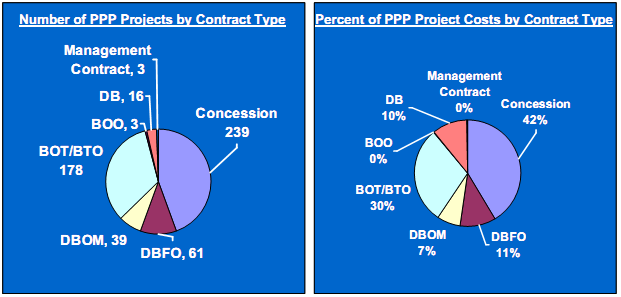
Exhibits 43 and 44 display the distribution of PPP road-related projects in other countries, excluding U.S., by facility type and contract approach, respectively, between 1985 and 2004.
Over that 20-year period there were 539 PPP road projects planned and funded in other countries, representing $282.5 billion in project costs. The majority of PPP projects in other parts of the world have used the following delivery approaches: concession, BOT. and BTO.
Exhibit 43 - Global Road-Related PPPs by Facility Type, Excluding the U.S. 20
(539 Planned & Funded Projects outside the U.S. worth $282.5 Billion between 1985-2004)
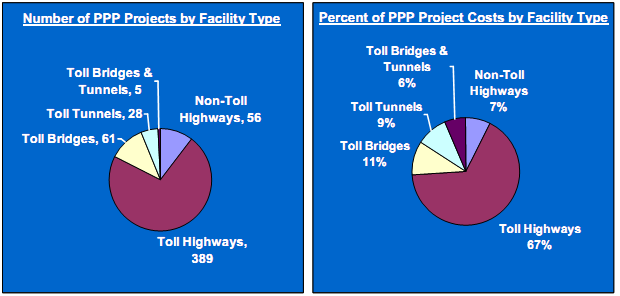
Exhibit 44 - Global Road-Related PPPs by Contract Type, Excluding the U.S. 21
(539 Planned & Funded Projects outside the U.S. worth $282.5 Billion between 1985-2004)
On the following page, Exhibit 45 shows the breakdown of road-related projects by global region and PPP contract type, excluding PPP projects in the U.S. to more clearly show the distinction between PPP use in other countries and in the U.S. (shown earlier in Exhibit 38). According to Exhibit 45, the regions which have investing the most in PPP contracts for road-related projects are Europe and Asia. In terms of average project cost, PPP road projects in the United States were about the same size as in Europe and Asia & Far East at about $670-690 million. By contrast, there was much greater use of concession and BOT/BOT contracting to deliver road projects worldwide, excluding the United States. This is particularly the case in Europe, Asia, Latin America, and Caribbean.
____________________________________________________________________________________
19 AECOM Consult, Inc. "Synthesis of Public-Private Partnership Projects for Roads, Bridges & Tunnels from Around the World - 1985-2004", prepared at the request of the Federal Highway Administration, August 30, 2005. Derived from Exhibit 4 on page 8.
20 AECOM Consult, Inc. "Synthesis of Public-Private Partnership Projects for Roads, Bridges & Tunnels from Around the World - 1985-2004", prepared at the request of the Federal Highway Administration, August 30, 2005.
21 AECOM Consult, Inc. "Synthesis of Public-Private Partnership Projects for Roads, Bridges & Tunnels from Around the World - 1985-2004", prepared at the request of the Federal Highway Administration, August 30, 2005.