VFM assessment
The VFM assessment involves comparing the net present value of the PSC costs with the total public sector costs of the proposed PPP structure as set out in the diagram below (see figure B.1). In advance of receiving detailed costings from private sector bidders, private sector costs under the PPP structure can be estimated by developing a "shadow bid." This allows an early assessment of VFM to help to avoid spending time going to the market with a transaction that could never be justified on a VFM basis. The net present value calculation should be based on the discounted cash flow of revenues and costs over the life of the project. The discount rate used should be the long-term cost of funds for the public sector authority.
It should be noted that in some cases, VFM cannot always be quantified. Qualitative aspects should also be considered including increased quality of service, speed of delivery and the long-term nature of the contracts. Where the differential with the PSC is quite small, these issues may result in the project VFM being viewed positively or negatively.
Figure B.1. Value for Money assessment
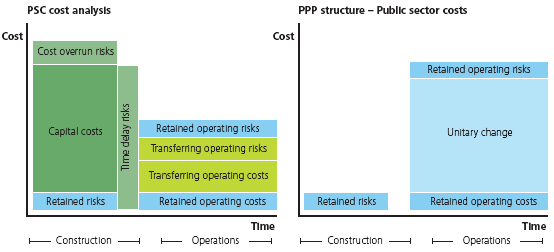
In certain instances, the VFM assessment can be more academic in nature given that without adequate public sector funds, the project may not be deliverable unless private sector funds are made available under a PPP structure. In those cases, the PSC should still be developed and the VFM analysis carried out to better understand the potential differential between the two options were public funds available. The key decision will depend on the affordability of the private sector option relative to the level of public sector funds available. While this is not ideal, it nonetheless is a reality in many countries around the world.