Capital Investments
The traditional or DBB method continues to be the dominating project delivery method for road projects in most of the countries. However, use of the innovative project delivery methods like Design-Build and PPP is increasing and more countries are adapting these practices. There have been numerous reports, positive results, and increased satisfaction with the Design-Build and PPP models. PPP is enticing many countries due to significant reductions in public spending and the private finance option makes it very attractive. Private finance and the PPP model should not be taken for granted, as it requires significant due diligence and understanding of all the consequences and is worthy of detailed investigation.
The main new methods uncovered during the study are the "Alliance model" and Early Contractor Involvement" (ECI). These are in the early stages and there is not enough quantitative results to make any conclusions at this time.
When progressing to these innovative models it can involve a great deal of effort and investigation because the concepts are quite new and there are significant issues that need to be considered. Results indicate that the benefits are significant; thus further development and continuous improvement of the models can be a worthy goal.
There are five main categories highlighting the practices and concepts that describe the key aspects of innovative contracting methods. Firstly, it should be realized that taking on these newer and innovative project delivery methods requires a significant learning process. The countries that have achieved those results have gone through a significant effort and process that has demonstrated strong leadership and good management practices. It should be noted that this was not achieved over night and there have been some road blocks and problematic areas, but continuous improvement should be used to determine the optimum model characteristics.
The transfer of risks is almost the most significant single issue. Most contractors are typically risk evasive and only the more advanced contractors seem to be accepting and managing these risks. This may be the reason for the some-what deliberate process as it takes champions in the industry to begin accepting risks through these newer methods. Once risk management is beginning to mature then there can be optimization of risks and a steady practice of which party is responsible to risks to a certain level.
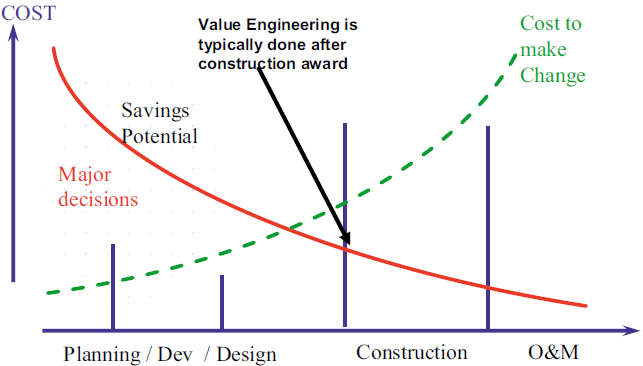
Involving the contractor into the project at the earliest possible planning phases is another aspect of innovating practices. This is where the constructability, cost optimization, any early impact to support innovative concepts into the design can be achieved. Usually this occurs after contract award when there can usually be very little changes to the design. Even better would be to involve the main actors in a spirit of true teamwork, partnership, and a leadership approach, which is the intent of the "Alliance model".
Quality and public values are very important and these key aspects should not be compromised. It is important to verify that the planning and design criteria are maintained to equal or better compared to traditional methods. Quality Control by contractors can be a form of monitoring quality during the construction phase, and having the correct level of performance specifications may increase the potential for innovations or alternative concepts. Also, by having significant quality elements in the tendering versus price may attract higher quality contractors as it requires a higher level of quality measurements. If allowed, a contractor and professional services interactive rating system, that is truly measuring some level of actual performance, would probably provide better results.
Finally, the road authority needs to understand that a well balanced procurement portfolio package will continue to sustain the market base of contractors and professional services. A proper strategy to incorporate the correct model for the appropriate project, compensation in the form of stipends to offset the higher tendering costs in the innovate models, non low-bid practices for these innovative models, and at the appropriate times to use restrictive bidding to maximum of three tenders for full pricing quotes after being short listed.
These can be summarized as follows:
Learning Process:
• As a logical progression, Design-Build should be the first model tested
• Takes time to implement
• Creating trust with industry takes time
• Continual learning process - reengineering the models
• Performance specifications should be developed for Design-Build and all related DB models
• Standardization of contracts & continuity amongst all regional road authorities
Risks:
• Knowledge and competence of risks
• Allocating risks to the proper party
• Risk optimization
Gains by Early Contractor Involvement (ECI):
• Using the Early Contractor Involvement (ECI) model
• Minimize design development to < 30% or less
• Potential of the "Alliance model"
Quality:
• QC by contractor
• Quality Based Selection criteria for contract award
• Performance Specifications
• Contractor rating program
• Professional services rating program
Procurement Portfolio:
• Having a proper procurement strategy & project portfolio
• Having expertise in all models & disseminated to all regional personnel
• Offset higher tendering cost by compensation via stipends
• Consider short listing to a maximum of 3 tenders for medium and large projects
• Consider the use of integrated phases for professional consultants for continuity
• No low bid tenders for the innovative models (except really small projects)
In addition to these findings and more of the authors' experience and recommendation, the following figure can help explain the need to have wise decisions made at the earliest outset of any project and one that can be delivered as quickly as possible. Many do not realize the total duration of a project can be 10 years or longer after project conception and moving through the governmental approval process, in which many events can occur before the project can be authorized and later on completed. Therefore, if it possible to use a situation where all customer needs, environmental aspects, public values, and "best for all attitude" can be used at the earliest concept then a picture might be developed as shown in Figure 22. (The light blue shaded area is the area where most decisions are finalized by the "Alliance team"). Thus, the method that comes close to this type of practice is the "Alliance model" as the key decisions are done early, has a leadership philosophy, a joint or real teaming approach, and a best for project attitude.
|
|
| TIME |
Figure 22 Effective & Efficient Decision Making Potential (VE curve)