Value for money mechanisms are needed
1.24 Although authorities should ensure that they obtain competitive prices by holding well run competitions, they will take additional comfort if there are contractual means for maintaining value for money during the contract period. For example, authorities will wish to ensure that the price they have agreed to pay in future years will not be in excess of future market prices for such services. Authorities can do this through benchmarking services, both in terms of price and quality, against market comparators, or through market testing. Where it is not possible to market test for new services, the authority and contractor need to have an agreed pricing system set out in the contract. Many contracts include value for money mechanisms (Figure 8) in line with the Treasury's Standard PFI contract terms.3
1.25 Profit and other gain sharing mechanisms can incentivise contractors to reduce costs to the authority, and allow the authority to share in profits made by the contractor through third party business generated by the deal. Such mechanisms may allow the authority to share in any profits above a certain defined level. A particular example where such gains may arise is where a project is refinanced.
7 |
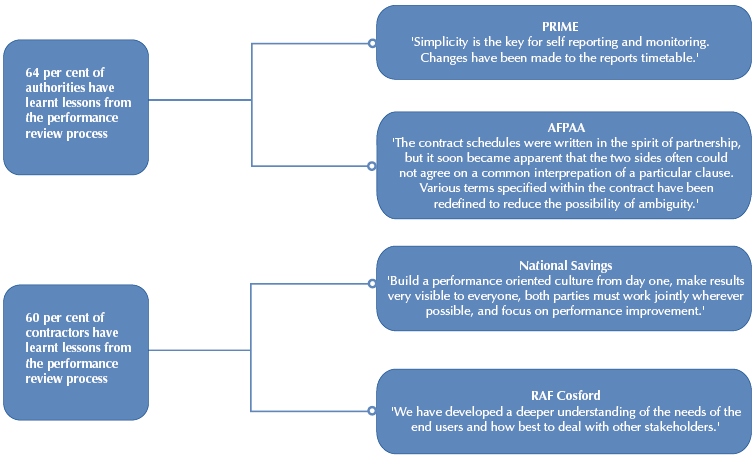
| Lessons learnt from performance reviews |
|
|
|
|
| Source: National Audit Office survey of authorities and contractors |
1.26 Any mechanism for profit sharing will require the contractor to supply relevant financial information to the authority. The inclusion of open book accounting will help to ensure that these value for money mechanisms are working as they should. It will also give the authority a greater understanding of the contractor's cost drivers and the impact on its profitability of authority actions or any changes made to the contract.
____________________________________________________________________________