Key risks to the project and to the Department's business needed to be managed
2.1 The role of risk management is to reduce the risk exposure of the organisation or project to a level that is acceptable. The use of formal risk management systems has been developing in UK government since the early 1990s, but all such systems will incorporate the following main elements:
■ Setting clear objectives: defining aims and objectives which can be used as a basis for identifying risks to the project and to the purchaser's wider business and reputation;
■ Risk Identification: listing each risk that could conceivably occur, and recording them for future management in a risk register or other control system. Risk registers are a common feature of successful Information Technology projects;
■ Risk assessment: assigning to each risk an estimate of the probability of it occurring and the impact on the project if it does; and
■ Risk mitigation, monitoring and control: including the allocation of each risk to a named individual or entity with the responsibility and authority to manage it, the selection by risk managers of options to deal with unacceptable risk, and regularly monitoring identified risks and the effectiveness of the actions taken.
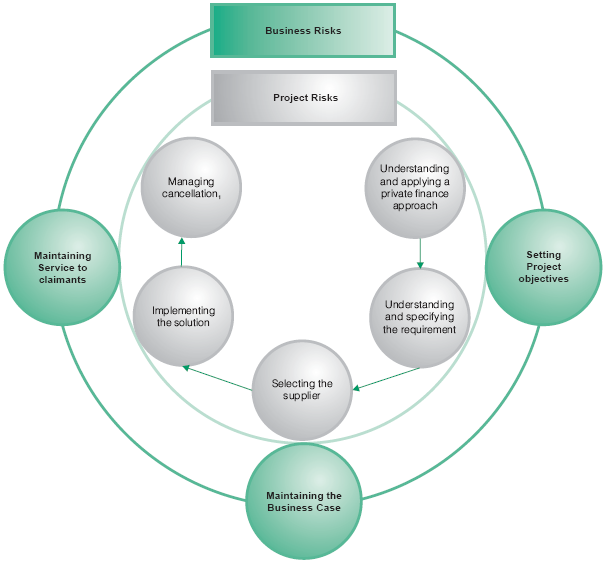
2.2 Some risks originate and are managed entirely within projects, but others arise from change in the customer's wider business. Figure 11 provides an overview of the key areas of risk in the Benefits Payment Card project.
Figure 11 |
|
An overview of the key risk areas of the Benefits Payment Card project | |
|
|
1. Paragraphs 1.20-1.27 | |