The first projects to value test services had limited guidance or help, but this has recently been addressed
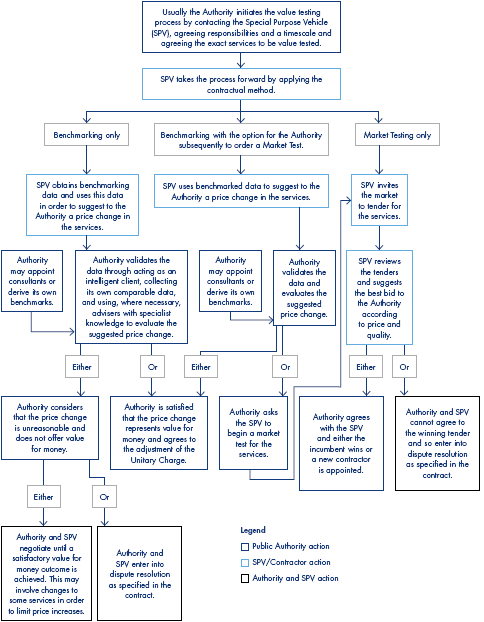
1.1 Benchmarking and market testing (Figure 4) are the methods used in PFI contracts to value test the cost and quality of certain services being provided by PFI contractors in order to ensure that the authority is getting value for money (Figure 5 overleaf). Value testing normally first occurs between five and seven years into operation and gives both the public and private sectors the opportunity to renegotiate the prices of the services tested in line with market rates. It provides an opportunity for the public sector to benefit if costs are falling. Conversely, if costs are rising, it allows the private sector to limit its exposure to cost increases above the rate of general inflation for which the private sector normally receives an annual price increase under the terms of a PFI contract. When value testing takes place this is also an opportunity for the public sector to renegotiate the specification of the contract.
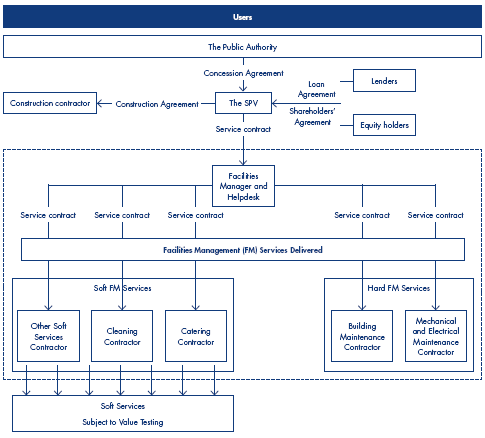
1.2 Benchmarking and market testing are primarily aimed at facilities management services such as catering and cleaning (Figure 6 on page 11) where there is no significant capital outlay in their performance. These services are often referred to as soft FM services (Figure 7 on page 12) and they constitute an important component of the whole life costs of the PFI project (Figure 1, page 5).
|
4 |
Treasury Definitions of Benchmarking and Market Testing |
|
|
Benchmarking is the process by which the project company contractor compares either its own costs or the costs of its subcontractors against the market price of equivalent services. If the costs are higher than market prices, a reduction in the price charged to the public sector should be made on an agreed cost-sharing basis to reflect the differential. If costs are lower than market prices, the project company must justify any price increase. |
||
|
Market Testing means the re-tendering by the project company of the relevant soft service so that the authority can test the value for money of that service in the market. Any increase or decrease in the cost of such a service following market testing should be reflected by an adjustment in the price charged to the authority. |
||
|
Source: Treasury |
||
|
5 |
The Alternative methods of the value Testing Process |
|
|
|
||
|
Source: National Audit Office |
||
|
6 |
Typical organisational structure of a PFI project highlighting the soft Fm component |
|
|
|
|
Source: National Audit Office |
|
1.3 Treasury guidance on benchmarking/market testing in PFI contracts first appeared in July 1999 in the Standardisation of PFI Contracts (SoPC) and has been revised and updated in subsequent versions of SoPC. These documents provide a commentary on the issues to be considered when drafting a PFI contract but they do not include required clauses so as not to be too prescriptive. This means that, especially in the early PFI deals let before 1999, contracts varied in the terms, if any, which they contained on how to proceed with a benchmarking or market test.
1.4 Recently the Treasury has published more authoritative guidance. It tasked PUK with researching the experiences of those early projects which had completed the process and it also took account of the initial findings of this NAO study. As a result, the Treasury introduced new guidance in October 2006, which supports project teams by providing more detail on the best process to be adopted during a benchmarking/market test, reflecting many of the issues we deal with in this report. In addition, in July 2006, the Department of Health published a Code of Best Practice for benchmarking and market testing in conjunction with the private sector representative body, the PPP Forum.
7 | Soft and Hard FM defnitions |
Soft facilities management (Soft FM) services are those services which are required for the operation of the building or facility. They include services such as cleaning, catering, porters, linen and laundry, security and reception. | |
Hard facilities management (Hard FM) services are those services responsible for the maintenance of the building or facility. | |
Source: National Audit Office | |