The Department scoped the project in a way that may not have maximised potential benefits
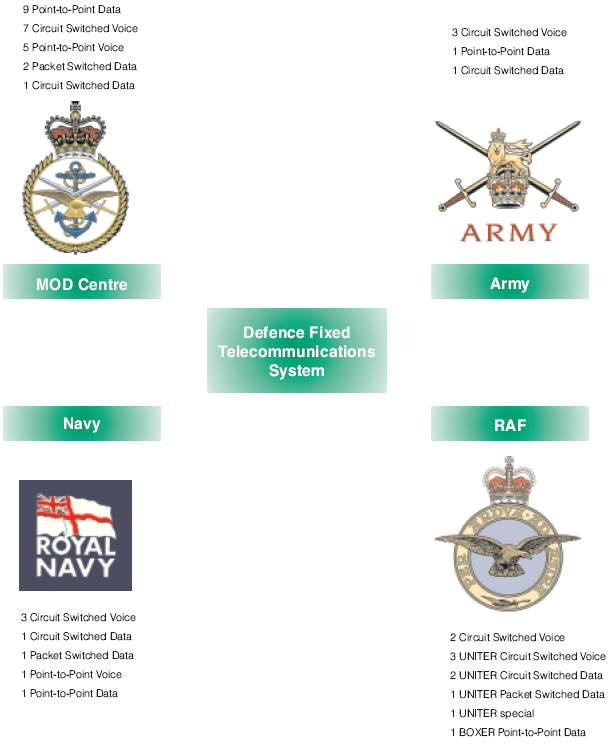
1.3 Prior to the letting of the contract, the Department's fixed telecommunications were operated separately by four organisations; the Army, the Royal Air Force, the Navy and the Department's administrative centre, leading to duplication of telecommunications service provision. Figure 1 shows the 46 previous services, grouped by organisation; these will all be provided by a single Defence Fixed Telecommunications System under the contract. Under the new contract, there will be a total of six fixed telecommunications services, as illustrated in Figure 2 on page 11.
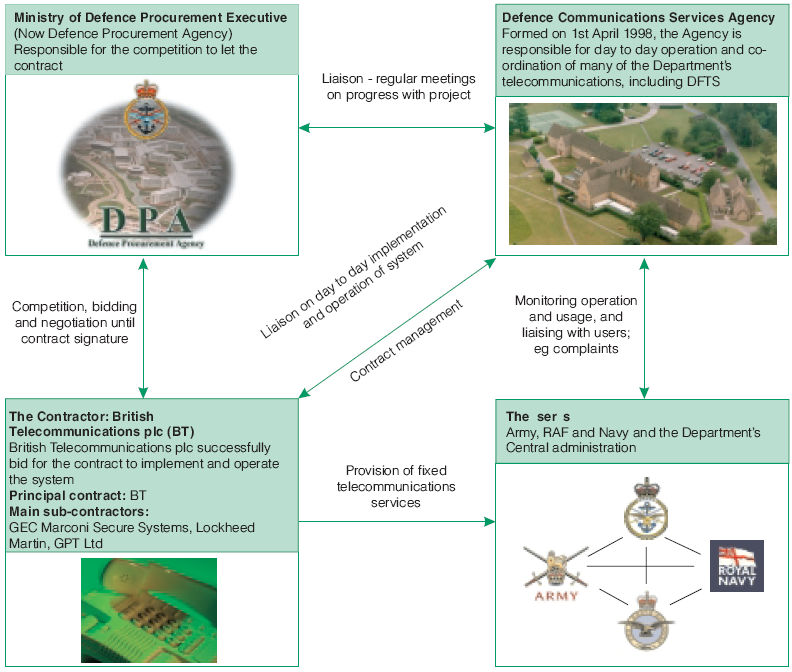
1.4 Since April 1998 a single organisation within the Department, the Defence Communications Services Agency, has been responsible for the day to day operation and co-ordination of many of the Department's telecommunications, including their fixed telecommunications. Figure 3 on page 12 shows the relationships between the main players in the contract.
|
|
Figure 1 | The previous services now included in the Defence Fixed Telecommunications System (DFTS) |
The figure shows the 46 previous services which are now part of the Defence Fixed Telecommunications System | |
Source: National Audit office | |
|
|
Figure 2 | The six types of telecommunication service |
Services 1 and 2: Point-to-Point Voice and Data All connections between terminals are by permanent lines.
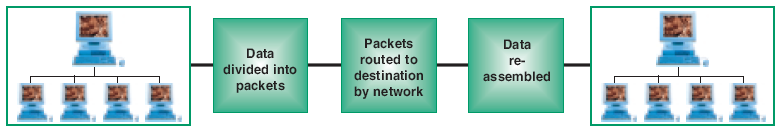
Service 3: Packet Switched Data Digital data transmissions are divided into groups of data or "packets" to allow them to share the network with other transmissions. Packets are re-assembled at receiving terminal to form original transmission. Allows more efficient use of network.
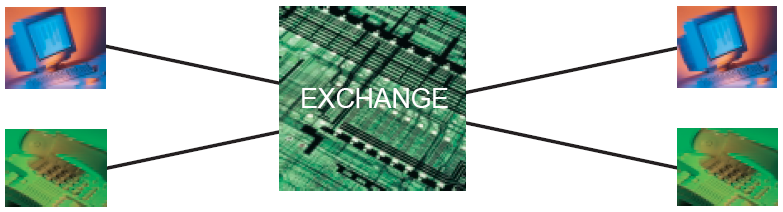
Services 4 and 5: Circuit Switched Voice and Data No permanent connections exist between terminals, but a digital circuit is established by a switching centre in an exchange when a transmission is made. This remains as a dedicated connection for the duration of the transmission. Once the transmission ends, the circuit is terminated.
Service : Local Area Network Interconnect (LAN Interconnect) Connects different Local Area Networks to allow transmissions between them. Local Area Networks typically serve a site, such as a Military base. Uses technology similar in principle to Packet Switched Service, but gives higher capacity and compatibility with the Internet. Source: National Audit Office | |
|
|
Figure 3 | The main players in the Defence Fixed Telecommunications System contract |
The figure shows the relationships between the main parties involved in the contract
| |
- The Department had identified scope for savings and efficiencies in their fixed telecommunications
- A strategic review of the project scope may have generated further savings
- But the Department considered that a different scope would delay savings
- They developed the project after considering various options for fixed telecommunications
- They chose a single network solution, with elements of other options