Standup Phase
Figure 2: Standup Phase
• Identify AF-wide (or MAJCOM, etc) Strategic Sourcing Opportunity (Centralized group (ESG or MAJCOM equivalent) conducts this assessment)
o Collect Air Force spend data from available sources:
n FPDS-NG
n GPC databases
n Suppliers
n CBIS
n MIPRS
o Segment AF spend into logical buying groups based on % of total Air Force Spend (or by % of supplies and services spend). These groups may be driven by Federal Supply Classification (FSC) codes but groups should include all commodities that are related by type of user and/or type of buyer. Other options by which to segment spend may include by market structure (it may make sense to group vehicle maintenance with boat maintenance if the companies have both skill bases) or based on a linkage analysis (may be beneficial to group airfield grounds maintenance with airfield operations so there is not a situation where one contractor can fail due to another contractor's poor performance). Also, consider qualitative factors that will influence the need for a commodity grouping (user group has expressed an interest; a large contract is expiring, etc.)
o Document the following statistics for each commodity (supplies or services) group:
n % of total AF spend
n % of AF Goods & Services spend
n # of total contract
n # of purchasing offices
n # of contractors
n Top 5 suppliers and % of AF spend and/or AF Goods & Services spend
n Top 3 purchasing locations (Base and Office) and % of AF spend and/or AF Goods & Services spend
o Evaluate selection criteria that reflect ease of implementation and expected benefit for each commodity group (see example: IAT Opportunity Assessment once you click into the file there are multiple tabs)
n Ease of spend analysis
n Ease of market analysis
n Level of skilled commodity experts
n Short and Long Term saving opportunities
n % Key supplier spend (Low <20%, Med 21 - 60%, High >60%)
n # of purchasing locations (Base and Office)
n Contracts vs. contractors (Low 1 - 1.5, Med 1.5 - 2, High >2)
n % AF Goods & Services Spend (Low <1%, Med 1 - 2%, High >2%)
n Short Term Win
n Emotional attachment
o Document other relevant information for each commodity group, such as:
n Existing Centers of Excellence (CoEs)
n Expertise in the field
n Work already completed
n Regionalization opportunities
n Spiral opportunities
n Small business opportunities
n Political relationships
n MAJCOM spend
n Constraints and concerns
o The relevant information should be captured and briefed to the official approving the strategy. This should include a high level summary and business case.
n Opportunity assessment process
n Current state of recommended opportunity
n Expected benefits/costs
n High level timeline for the effort
n Needed resources
n Constraints and concerns
n Total cost of ownership
• Approve the Strategic Sourcing Opportunity
o The authorities for this step will vary but ultimately should include AQC (or designee) and the lead for the functional commodity. For example, the IT commodity council opportunity was approved by AQC and the CIO. Installation opportunities will be presented to the IAT governance structure where the Executive Committee will have the final approval. The governance structure consists of AQC and functional membership. MAJCOM strategic sourcing initiatives should follow the same pattern with the A7K and MAJCOM functional lead approving the initiative.
o As part of the approval the authorities are also agreeing to provide the needed resources for the effort
• Prepare and Gain Approval of the Charter
o Define the authority under which the council shall operate. This will aid in the establishment of goals and the scope in which the council operates. Recent industry examples reported that companies setting up commodity teams without the CEO's participation and leadership achieved 50 percent less savings than when the CEO led the effort.
o Define the primary goals and objectives of the council. Develop the charter document in accordance with the required/recommended information as detailed here.
o Meet with the appropriate approval authorities for the specific commodity and obtain approvals and signatures.
• Assign Resources
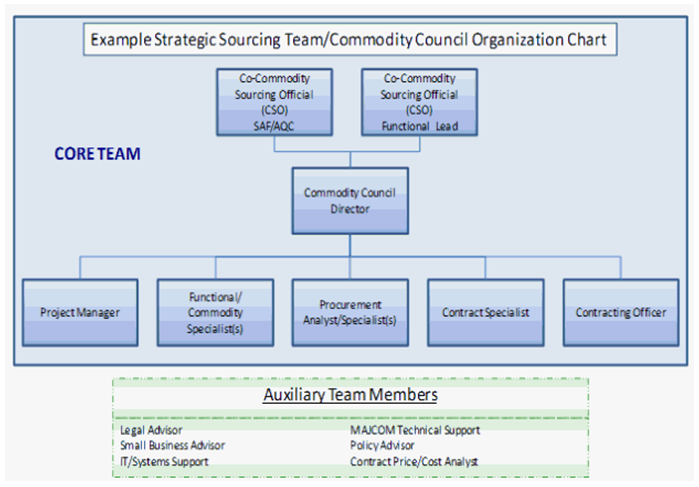
o Cross-functional representatives may be selected to ensure adequate representation from across the Air Force. The commodity council/strategic sourcing team should contain commodity expertise, as well as knowledge in procurement, technology, market analysis, project management, business processes, acquisition strategy, and analysis. An example is provided in Figure 3, but each team may be different.
o The exact core team size and composition may vary according to the commodity and anticipated associated workload. The size, complexity and magnitude of the commodity dictate whether or not a particular council/team warrants full-time or part-time personnel and the number of extended members needed. The councils/teams also need administrative support for scheduling, documenting, and tracking sessions.
o Core team members are expected to fill full-time positions throughout CC/SS team operations, while auxiliary team members provide expertise on an ad hoc basis, depending on the stage of the process or the nature of a particular commodity spiral group. Each Director needs to determine what roles are essential for the specific CC/SS team. In addition, some roles may be combined if a single individual possesses the adequate qualifications and the responsibilities can be met with that level of effort.
o Overall, each commodity council/SS team member needs to have a basic understanding of the Air Force Contracting vision, possess basic knowledge of the strategic sourcing concept, be committed to the success of the Commodity Council and be available to fulfill the requirements of their position (whether full-time or part-time).
o Identify MAJCOM Representatives:
n Select representatives to provide appropriate representation based on the goals for the council. The Director should determine how many Headquarters staff experts, operational experts, support personnel, and contingency experts are needed.
n Coordinate with MAJCOM, DRU, and FOA headquarters to adequately fill roles. Headquarters may select representatives or a Director may request an individual by name, when a person has the required expertise.
n Emphasize the time and effort required for council participation. These efforts require time and often there is a sense of urgency to complete the tasks at hand. An individual's role on the council may be their primary job until the first strategy is approved.
n Identify auxiliary team members who serve on an ad-hoc (as needed) basis.
o Review the SharePoint site for templates, best practices and lessons learned from various other strategic sourcing teams/commodity councils that have gone through the process. Once the team has been established conduct a kickoff meeting detailing roles and responsibilities, rationale, schedule and goals. Also, set up the team to take or participate in any needed training. There are CLC overviews of Strategic Sourcing CLC 108; Spend Analysis - CLC 110 and Market Research - CLC 004 as well as just-in-time training modules owned by the IAT PMO.
Figure 3: Commodity Council Organization