5. Advancing through Science, Technology and Innovation (STI)
A "whole-of-government" approach will be pursued to achieve competitiveness. Thus, the government will strengthen vital factors that highly contribute to the advancement, distinction, satisfaction and demands in the domestic and international markets "Science, Technology and Innovation" (STI), and "Quality".
a. The government shall continue to implement the national innovation strategy called Filipinnovation. This will enable the country to achieve (1) a competitive and multi-disciplinary work force competent in producing value-added knowledge-based services of global standards; (2) competitive local firms driven by or borne out of constant innovations brought about by increased R&D; and (3) a public policy environment that ensures continuous innovation not only through executive, legislative and judicial initiatives but through local government programs. It will promote the usage of Information and Communications Technology (ICT) in enterprises. Filipinnovation focuses on: (1) strengthening human capital investments for STI; (2) stimulating STI; (3) enhancing management of the STI system; and (4) upgrading the Filipino mindset in S&T. Since the strategy/policy imperatives are interconnected, it shall be coordinated and harmonized to create necessary conditions to deepen and consolidate STI capacity.
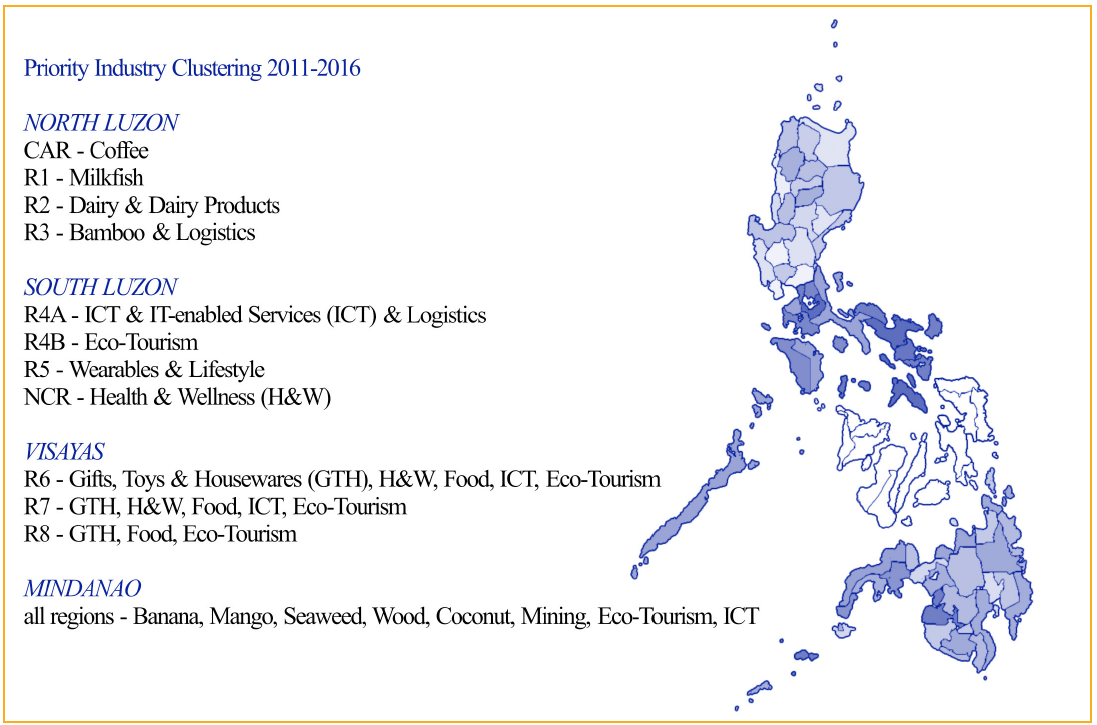
Figure 3.6: Industry Cluster Map
b. The government shall set up a National Quality Infrastructure to integrate and coordinate series of activities involving metrology, standardization, testing, and accreditation and certification. It will provide procedural landscape for products and services of enterprises, particularly SMEs, to meet quality requirements. It will guarantee competitiveness in the national and international markets through quality certification.
c. STI, a crucial factor for productivity, competitiveness, job creation, sustainable development and poverty alleviation will also pursue R&D initiatives:
• Address opportunities for STI professionals;
• Address structural gaps in the STI and R&D sectors such as inefficiencies in the structure of incentives and allocation of R&D resources that are obstacles to new programs and activities which could help attain STI and R&D goals;
• Facilitate new STI policies needed to boost productivity, economic growth and job creation through increased knowledge-intensive economic activities while maintaining social cohesion;
• Foster tie-ups between industry and the higher education institutions to strengthen the effective transfer of appropriate technology and advanced skills needed by the industry and for the production of higher value goods and services;
• Facilitate and utilize sufficient information on the scientific and technological experiences and know-how of other countries;
• Establish e-centers to enhance access to knowledge and technology, particularly in rural and remote areas;
• Implement programs and tools to support and respond to climate change and disaster risks incidents especially for fishers and agri/marine farmers; and
• Policy backup and enforcement mechanisms for existing laws require bolstering and institutionalizing in close collaboration with neighborhoods.