Alternative Fuels
Biofuels Program. As of the first half2010, the DOE had accredited 14 biofuel producers (12 for biodiesel and 2 for bioethanol). The 12 biodiesel producers have a combined production capacity of 395.6 million liters per year. The total sales of biodiesel (CME) blend was 130.9 million liters in 2009 and 54.2 million liters in 2010. Actual diesel fuel displacement from biodiesel in 2009 translates to an equivalent foreign exchange savings of US$34.9 million.
On the other hand, Leyte Agri Corporation, the country's first ethanol facility, and San Carlos Bioenergy Inc., Southeast Asia's first dedicated ethanol distillery with an integrated co-generation power plant, have a combined production capacity of around 49 million liters of ethanol annually. Both plants together sold 23.1 million liters in 2009, equivalent to foreign exchange savings of US$10.1 million from gasoline displacement. In the first half of 2010, 9.2 million liters of ethanol were sold to oil companies. By end-2010, Roxol Bioenergy's ethanol plant would have provided an additional capacity of 30 million liters per year, bringing total annual ethanol production to about 79 million liters.
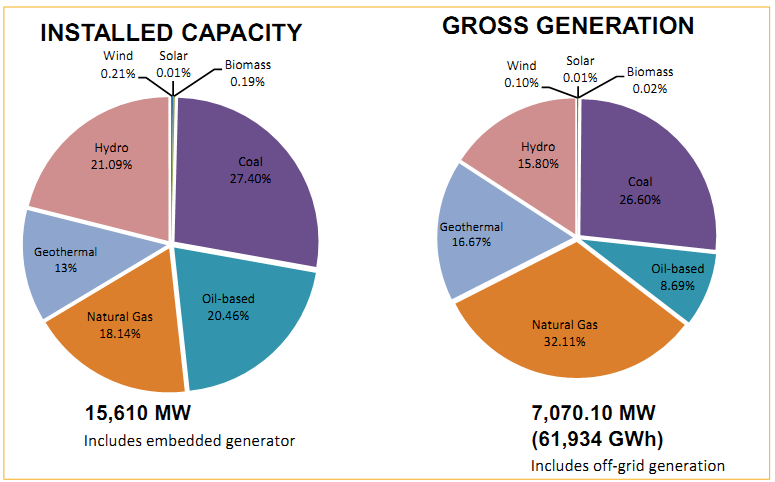
Figure 5.4. Philippine Capacity and Gross Generation: 2009
To meet the technical requirements of the program and ensure continuous research and development support, the DOE provided counterpart funding of PhP50 million for the establishment of a vehicle-testing facility located at the Department of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory, UP-Diliman.
Auto-LPG Program. In support of the government's Auto-LPG Program, the Development Bank of the Philippines (DBP) has included the auto-LPG initiative in its "Clean Alternative Transport Fuel Financing Program," which provides reasonable financing packages for auto-LPG related activities such as acquisition of auto-LPG vehicles. The Land Transportation Franchising Regulatory Board (LTFRB) also extended by two years the franchise of taxis that converted to auto-LPG. These schemes promote large-scale conversion of taxi fleets and encourage new player participation in the program.
As of first half of 2010, there were about 18,731 converted vehicles nationwide running on LPG and 217 auto-LPG dispensing stations (72 garage-based). The sales growth of auto-LPG products registered an equivalent reduction of CO2 emissions by 214,664 metric tons (MT) and 48,789 MT for 2009 and the first quarter of 2010, respectively. Moreover, the 293 LPG-converted tricycles nationwide have an equivalent reduction of 495,521 kilograms (kg.) of carbon dioxide.
Natural Gas Vehicle Program for Public Transport (NGVPPT). The alternative use of natural gas in the transport sector is being pursued through the NGVPPT. From a minimal volume of CNG utilization in 2007 following the inauguration of the pilot mother and daughter refueling system, the total consumption of natural gas for the transport sector already reached 18.1 Million Standard Cubic Feet (MMSCF) in 2009.
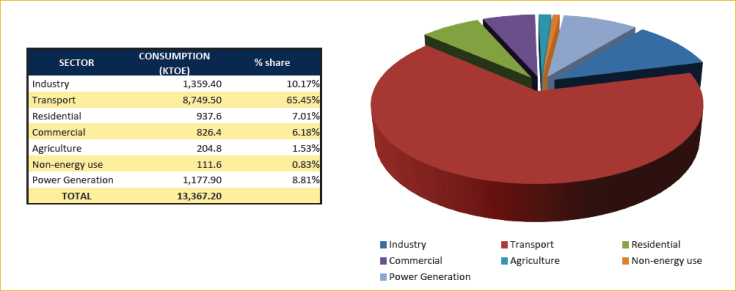
Figure 5.5. 2009 Sectoral Oil Consumption; 2009
As of first half of 2010, there were 7 accredited bus operators and 34 CNG buses plying the routes of Southern Luzon and Metro Manila. An additional 27 buses are under testing and evaluation. The CNG daughter refueling station operates in Barangay Sto. Tomas, Biñan, Laguna.
To sustain developments in the industry, a joint undertaking with the Polytechnic University of the Philippines (PUP) was initiated to establish the first Natural Gas Institute in the country. The said Institute is envisioned to develop the industry and enhance local capacity to support the emerging natural gas industry and provide the necessary capacity building needs of the industry.