MODULE 3 Implementing PPP Projects
This module provides guidance on each stage of developing and implementing a PPP project-from initially identifying candidate projects, to managing PPP contracts through the project lifetime. Section 2.3.1: PPP Process introduced the overall PPP development and implementation process, also shown in Figure 3.1: PPP Development and Implementation Process. This module describes each stage in the PPP process in more detail, providing links to resources, tools, and further guidance for PPP practitioners.
Governments only want to develop 'good' PPP projects-that is, PPPs for projects that are cost-benefit justified, where the PPP provides better value for money than traditional public procurement, and is fiscally responsible (see Box 3.3: PPP Project Appraisal Criteria). However, whether a project meets all these criteria cannot be fully assessed until the project is fully designed, and cannot be confirmed until bids are received. This creates a Catch 22 situation-the government does not want to incur the considerable costs of developing a PPP unless it knows the project meets the criteria, but cannot tell if it meets the criteria until the project has been developed.
Successful PPP programs tackle this problem through an iterative approach, of progressively more rigorous screening at successive stages of project development. The idea is that projects must seem likely to be suitable for development as a PPP before any public money is spent on them. Then, the processes of preparation is broken into successively more intensive and expensive phases, with a check before each phase that it seems likely that the project will continue to meet the criteria required for all successful PPPs.
Figure 3.1: PPP Development and Implementation Process
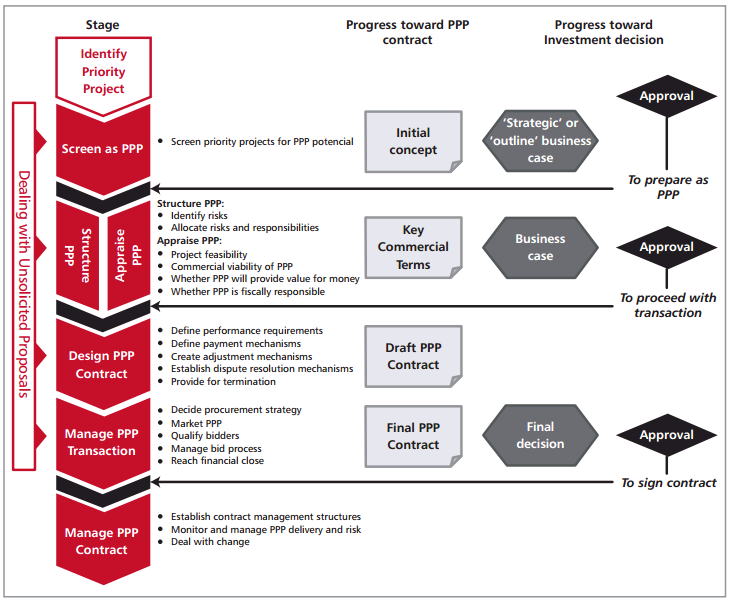
This module describes this iterative process for developing a PPP, as follows:
• Project identification and screening-the process of developing and implementing a PPP is typically preceded by identifying a priority public investment project, typically through a public investment planning and project selection process. At some point in this process some or all proposed public investment projects are then screened for their potential as a PPP
• Candidate projects that survive the 'screening' are then developed and appraised. Again, this is an iterative, or multi-stage, process-hence appraisal and structuring are shown in parallel in Figure 3.1 above. Because appraisal and structuring are different things conceptually, the Reference Guide discusses first one (Section 3.2 on appraisal) and then the other (Section 3.3 on structuring). In reality, projects will typically be partially structured, then partially appraised, then more fully structured, and more fully appraised. Different countries break up these iterative steps differently. The end result, often called a 'Business Case', is typically the basis for approval to proceed with the PPP transaction
• Before the PPP transaction can be implemented, the draft PPP contract needs to be prepared-further refining the PPP structure by setting out its details, in appropriate legal language. Section 3.4 sets out some key elements of PPP contract design
• Managing a PPP transaction is a complex process. A well-designed and well-implemented transaction process is central to achieving value for money from the PPP. As described in Section 3.5: Managing PPP Transactions, this can include marketing the PPP, checking the qualifications of bidders, inviting and evaluating proposals, interacting with bidders during the process, and identifying and finalizing the contract with the selected bidder. At the end of the transaction, after bids are received and the contract agreed, government will finally know the cost and risks in the PPP project. At this point it may be checked once more to ensure it still meets the PPP criteria
• As an alternative approach to originating and developing PPP project ideas, some governments accept unsolicited proposals for PPP projects from private companies, as described in Section 3.6.
• Having executed the contract, the PPP enters the final and longest 'stage'-managing the contract throughout its lifetime, as described in Section 3.7.
This guidance module is far from an exhaustive resource-developing a PPP is a complex process and every project has vagaries. Public officials should hire experienced advisors when implementing a PPP project. The World Bank toolkit for hiring advisors for PPP in infrastructure provides extensive guidance on engaging and managing advisors.
Overall guidance on implementing PPP Projects
As described in Module 2, some governments develop detailed guidance material or manuals for PPP practitioners. The World Bank and other multilateral institutions have also published guidance material and toolkits on developing and implementing PPP projects, including sector-specific materials.
The table below lists some of the best PPP guidance documents published by governments with successful PPP programs, and by multilateral organizations. The relevant sections of these manuals are included as 'further resources' for each PPP stage in the sections below.
| Key References: Practical Guidance on Implementing PPP Projects | |
| Reference | Description |
| PPP Program Material |
|
| Australia, Infrastructure Australia (2008) National PPP Guidelines: Practitioners' Guide (Vol. 2) Canberra | Detailed guidance material for implementing agencies on how to implement PPP projects under the national PPP policy, including project identification, appraisal, PPP structuring, the tender process, and contract management. Includes detailed guidance in annexes on technical subjects |
| Colombia, Ministerio de Hacienda y Crédito Público (2010) Manual de Procesos y Procedimientos para la ejecución de Asociaciones Público-Privadas (PPP Manual) Bogotá | A guide for civil servants from national, regional and local governments. It sets out in detail the processes and requirements for identifying, assessing, preparing, tendering, and implementing PPP contracts |
| India, Ministry of Finance (2011) PPP Toolkit for Improving PPP Decision-Making Processes, New Delhi | Online toolkit describing PPP process and providing sector-specific guidance and tools for practitioners on all stages of managing a PPP |
| Brasil, State of Rio de Janeiro, Conselho Gestor do Programa Estadual de Parcerias Público-Privadas - CGP (2008) Manual de Parcerias Público-Privadas - PPPs (PPP Manual) Rio de Janeiro | A guide for civil servants of the State of Rio de Janeiro on developing and implementing PPP. Defines PPPs, and provides guidance on drafting a preliminary proposal, carrying out detailed technical studies, managing the tender, and managing the contract |
| South Africa, National Treasury (2004) Public Private Partnership Manual, Johannesburg | Manual for implementing agencies setting out in detail the process and requirements for developing and implementing PPPs in accordance with the national PPP regulation. Includes modules on PPP Inception, the PPP Feasibility Study, PPP Procurement, and Managing the PPP Agreement. Includes tools and templates in annexes for use at each stage |
| France (2011) Les Contrats de Partenariat: Guide Methodologique, Ministry of Economics, Finance, and Industry | A detailed Methodological Guidebook for PPPs, sets out the rationale for PPP; the process for developing and implementing a PPP; and provides detailed guidance for each step |
| Other Guidance Material and Toolkits | |
| Kerf, Gray, Irwin, Levesque, Taylor & Klein (1998) Concessions for Infrastructure: A guide to their design and award, World Bank Technical paper 399 | Describes and provides examples on several of the important steps in developing and implementing PPPs-focusing on user-pays PPPs, or concessions. Includes sections on detailed design, the tender process, and the institutional (regulatory) structure for contract management |
| Farquharson, Torres de Mästle, and Yescombe, with Encinas (2011) How to Engage with the Private Sector in Public-Private Partnerships in Emerging Markets, World Bank/PPIAF | Describes and provides guidance on the whole PPP process, highlighting the experience of developing countries. Briefly covers project selection; the focus is on preparing and bringing the project to market, and engaging with the private sector |
| World Bank (2009) Online Toolkit for Public Private Partnerships in Roads and Highways | Module 5: Implementation and Monitoring provides guidance and links to further material on project identification, feasibility studies and analysis, procurement, contract award, and contract management |
| World Bank (2006) Approaches to Private Participation in Water Services: A Toolkit | Provides guidance on the PPP process, from planning and upstream policy, to the detail of structuring a PPP and implementing a transaction. Focus is on user-pays PPPs in the water sector |
| World Bank (2007) Port Reform Toolkit 2nd ed. Washington, DC | Provides guidance on several aspects of PPPs in the port sector-including guidance on risk identification, financial analysis, contract structuring, and contract management approaches |
| Flanagan, J. & Nicholls, P. (n.d.) Public Sector Business Cases using the Five Case Model: a Toolkit, London | Provides guidance on how to produce business cases. It is intended to help anyone involved with, or overseeing, a project to understand the work that is necessary to prove a case for investment |
| United Kingdom, Her Majesty's Treasury (2008) Competitive Dialogue in 2008: OGC/HMT joint guidance on using the procedure, London | Provides an outline of a general structure which is applicable to most Competitive Dialogue procurements in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland |
| United Kingdom, Her Majesty's Treasury (2007) Standardization of PFI Contracts: Version 4, London | The report serves three main objectives: 1) to promote a common understanding of the main risks which are encountered in a standard PFI contract; 2) to allow consistency of pricing across a range of similar projects; and 3) to reduce the time and costs of negotiation by enabling all parties concerned to agree a range of areas that can follow a standard approach without extended negotiations. |
| India, Ministry of Finance (2010) PPP Toolkit for Improving PPP Decision-Making Processes, New Delhi | This is an online toolkit designed to improve decision-making for PPP practitioners across India |
| India, Ministry of Finance (2008) Guidelines for Formulation, Appraisal and Approval of Central Sector Public Private Partnership Projects, New Delhi | This is a compendium which brings together the guidelines notified by the central Government of India for the formulation, appraisal and approval of central sector PPP projects |
| India, Ministry of Finance (2007) Model Request for Proposal for PPP Projects, New Delhi | This report provides a Request For Proposal for PPP Projects template as well as a short memorandum on the guidelines for invitation of financial bids for PPP projects |
| India, Ministry of Finance (2009) Model Request for Qualification for PPP Projects, New Delhi | This report provides a Request For Qualification for PPP Projects template as well as a short memorandum on the revised RFQ for pre-qualification of bidders for PPP projects |
| India, Ministry of Finance (2006) Guidelines for determining eligibility of proposals for financial support to Public Private Partnerships in infrastructure under the Viability Gap Funding Scheme, New Delhi | This report provides a template with a checklist for financial support to Public Private Partnerships in infrastructure under the Viability Gap Funding Scheme |
| India, Ministry of Finance (2008) Panel of Transaction Advisors for PPP Projects: A Guide for Use of the Panel, New Delhi | This users' guide describes the processes and the tasks involved in appointing a Transaction Advisor for a PPP transaction using the Panel |