The Emergence of Infrastructure PPPs in Asia
The participation of the private sector in infrastructure in Asia has its origins in the wave of privatizations in the 1980s and 1990s. Back then, rising evidence of inefficient public spending, poorly managed state-owned enterprises, and widespread fiscal and debt crises called for a new model of economic development led by the private sector and market liberalization. Henckel and McKibbin (2010) note that the private sector's involvement in infrastructure, either exclusively or through PPPs, is motivated by inefficiencies in public projects, such as cost blowouts, planning and construction delays, safety problems, and a lack of innovation and technological advancement.
Figure 2.1 shows the gradual rise of PPP transactions in developing regions since the mid-1980s. The World Bank's Private Participation in Infrastructure Database records 6,124 infrastructure PPP projects, totaling $1.7 trillion from 1985 to 2015 among 139 low- and middle-income countries. Infrastructure PPP projects in developing Asia climbed rapidly during the 1990s. From 1990 to 2015, the region closed more than 3,000 infrastructure PPP projects, totaling $652 billion in committed investment.
Figure 2.1: Infrastructure PPP Projects in Developing Regions, 1985-2015
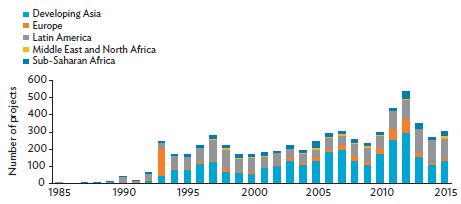
Source: World Bank, Private Participation in Infrastructure Database (accessed 20 March 2017).
Within developing Asia, building and upgrading infrastructure via PPPs considerably varies (Figure 2.2). The surge in financial closure of PPPs in 2011 and 2012 came mostly from East Asia and South Asia. PPPs in Central Asia and the Pacific were relatively few over this period, but those in Southeast Asia showed a rising trend, especially in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines, and Viet Nam. By country, India and the People's Republic of China had the highest number of infrastructure PPPs, totaling a combined 2,145 projects in the period. These accounted for more than half of the region's total number of infrastructure PPP projects
Figure 2.2: Infrastructure PPP Projects in Developing Asia, 1985-2015
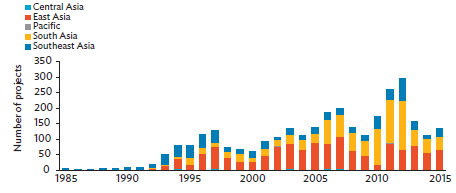
Source: World Bank, Private Participation in Infrastructure Database (accessed 20 March 2017).
Figure 2.3 breaks down developing Asia's infrastructure PPPs by sector. Most projects were in energy and transport. Energy investments have declined since 2013, an indication of the sector's growing maturity and lessening reliance on PPP support.
Figure 2.3: Infrastructure PPP Projects by Sector in Developing Asia, 1985-2015
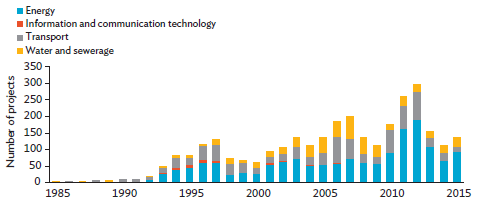
Source: World Bank, Private Participation in Infrastructure Database (accessed 20 March 2017).