Failed PPP Projects in Developing Countries
The World Bank's Private Participation in Infrastructure Database defines a cancelled PPP project as one in which the private partner has quit a partnership, either by selling or transferring the economic interest back to the government before fulfilling the contract terms. A distressed PPP project, also using the World Bank's definition, is when a public sector partner or private sector operator has either requested a contract to be terminated or requested international arbitration to settle a dispute. This chapter uses both definitions in its analysis of project failure. The stakes are high when this happens: public services can get disrupted, it discourages private investment in other PPPs, and-for certain projects-may require higher risk premiums.
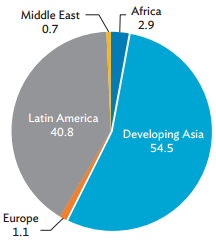
The World Bank's Private Participation in Infrastructure Database shows that 259 PPP projects in developing countries worldwide were cancelled, and 67 were distressed, out of 6,273 PPP projects from 1991 to 2015. This might seem small, but it should be noted that only 216 projects were completed in the period. More than half the cancelled projects were in developing Asia (Figure 3.1). Globally, the cancelled projects had initial investments of $76.4 billion, 4.4% of the $1.7 trillion committed investments.
Figure 3.1: Cancelled PPP Projects by Region, 1991-2015
(% share to total cancelled projects)
PPP = public-private partnership.
Notes:
1. Includes only low- and middle-income countries.
2. Excludes privatizations and merchant projects that do not include government guarantees or that operate in a liberalized environment.
3. Projects in the World Bank's Private Participation in Infrastructure Database must be at least 20% privately owned; state-owned enterprises are considered public.
Source: World Bank, Private Participation in Infrastructure Database (accessed 28 March 2017).
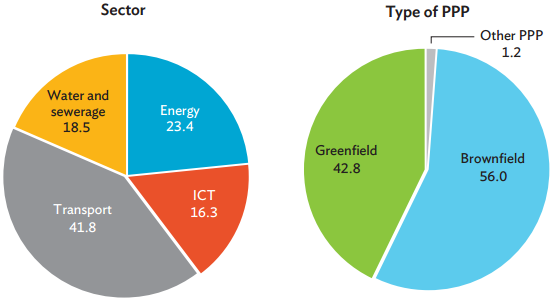
For developing Asia, most failed PPPs were in transport and energy (Figure 3.2). Within a sector, information and communication technology had the highest failure rate-25% or 14 failed projects out of 41 covered in the database in the review period.
Figure 3.2: Cancelled PPP Projects by Sector and Project Type
by Investment, 1991-2015
(% share total cancelled projects)
ICT = information and communication technology, PPP = public-private partnership.
Notes:
1. Other PPP includes management and lease contracts and partial divestitures.
2. Includes only low- and middle-income countries.
3. Excludes privatizations and merchant projects that do not include government guarantees or that operate in a liberalized environment.
4. Projects in the World Bank's Private Participation in Infrastructure Database must be at least 20% privately owned; state-owned enterprises are considered public.
Source: World Bank, Private Participation in Infrastructure Database (accessed 28 March 2017).
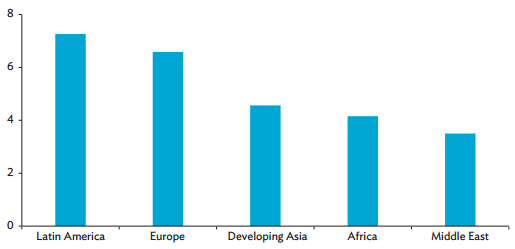
On average, project cancellations in developing Asia occur 5 years after financial closure, which is typically during the final stage of project construction (Figure 3.3).
Figure 3.3: Mean Duration of PPP Project Cancellations
PPP = public-private partnership.
Notes:
1. Duration is measured as the time difference from the financial closure year (that is, the year in which private sponsors legally entered an agreement to invest funds or provide services) through to the year in which the project was cancelled.
2. Includes only the low- and middle-income countries.
Source: World Bank, Private Participation in Infrastructure Database (accessed 28 March 2017).