Nonparametric Analysis: Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves
In survival analysis, it is very useful to look at Kaplan-Meier survival curves before proceeding to more complicated analyses to gain an insight into the intuitive graphical representation of the survival function for all the categorical variables. The Kaplan-Meier estimator is a nonparametric technique for estimating survival function-the probability of surviving past certain times in the sample, taking censoring into account.
The Kaplan-Meier estimate of  .
.
If no failures at time and if one or more failures at time
and if one or more failures at time where n(t0) is the number of projects at risk at the start time (t0) and d(t) is the number of failures at time t. The estimate does not change between events, nor at times when only censoring occurs. It drops only when a failure is observed. When writing the t(i) as the ith ordered event time, and d(i) and n(i) accordingly, the Kaplan-Meier formula can be written:
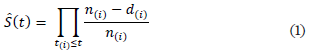
where Ŝ(t) = 1 for t < t(i). n(i) is the number of projects at risk at the ith ordered start time (t0) , and d(i), is the number failures at the ith ordered time (t). The total probability of survival until that time is calculated by multiplying the survival probability at all periods preceding that time. The Kaplan- Meier curve shows the cumulative probability function. The lengths of the horizontal lines along the x axis of serial times represent the survival duration, and the cumulative probability of surviving a given time is on the y axis. The Kaplan-Meier curves estimate the probability of a PPP project surviving based on contract type, unsolicited proposal by award type, MDB participation, sponsorship, government support, and type of PPP.