Financial Analysis - Capital and Capital Related Transaction Costs
2.5 Capital and transaction costs for the Pilot PPP Schools Bundle are as per the financial close figures within the Financial Model and have been spread over the 25-year Concession period in line with the actual payments of the financing. Construction variations have not been included in the costs from the Financial Model. Transaction costs include the Design Team fees and costs associated with gaining planning, contracting and mobilisation payments for service providers.
2.6 Capital and transaction costs for the Conventional Schools are fully funded by the DoE at the time of construction and are as per the final account costs provided by DoE. They therefore do include construction variations; however, these were minimal according to discussions with the relevant persons. Costs have been inputted into the actual years the costs were incurred, with an estimated split over the years in the form of a typical 'S Curve' form of construction expenditure as agreed with the DoE. All costs are actual except for the costs for equipment and fittings and furnishings at one Conventional School which are an average of costs for the other three Conventional Schools.
Figure 2.4 - Capital and Transaction NPV (€/m2)
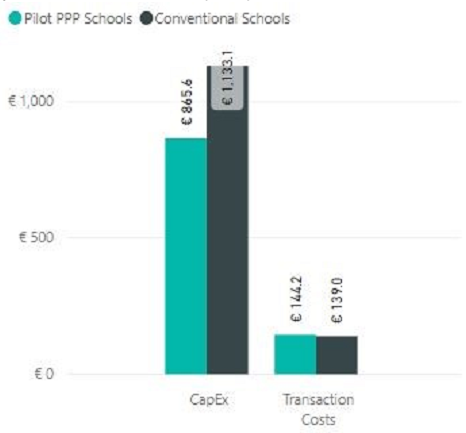
2.7 The Pilot PPP Schools Bundle construction costs are 24% lower than the Conventional School costs, whereas PPP transaction costs are 4% higher than Conventional School costs. When considered together, PPP CAPEX costs are 21% lower (Figure 2.4).
2.8 Whilst this conclusion shows that the PPP offers some 21% better value from an NPV perspective due to the amortisation of the repayments, the financing costs of the CAPEX are not considered in this analysis and would be expected to diminish the benefit achieved from the lower NPV capital costs. However, the higher cost of finance also must also be weighed against the risk transfer to the private sector, which is not costed within the financial analysis.
2.9 The debt cost for the Pilot PPP Schools Bundle, based on information provided by the NDFA, is understood to be c.6%. Debt makes up the majority of funding for the scheme.