Effect of Condition on Residual Life
2.28 Residual Value4 is the cost of replacing an asset with its modern equivalent less deductions for physical deterioration. The Residual Value is a key element for consideration of the whole life cost, as at the end of the PPP contract the schools are handed back to the DoE. The Residual Value at the end of the 25-year analysis period is greater for each of the Pilot PPP Schools than the Conventional Schools. This is due to the poorer condition of the Conventional Schools when compared with the Pilot PPP Schools as assessed in the condition survey, and the higher level of Backlog Maintenance works required.
Figure 2.11 - Backlog Maintenance by Group (€/m2)
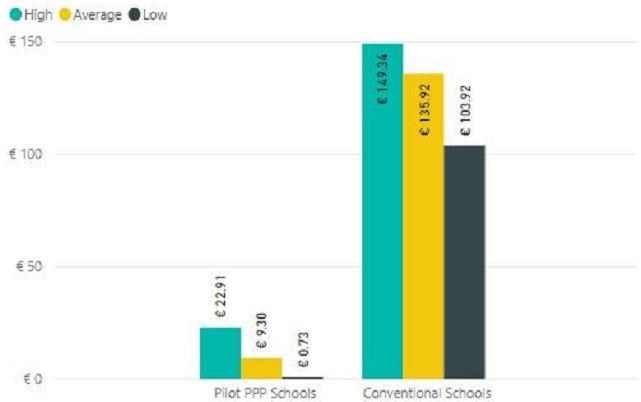
2.29 As shown in Figure 2.11, Backlog Maintenance at the Conventional Schools is significantly higher than at the Pilot PPP Schools. This is indicative of maintenance and/or Lifecycle replacement works not being undertaken as and when required, as evidenced during the condition surveys.
2.30 Backlog Maintenance is minimal across the Pilot PPP Schools Bundle. Where Backlog Maintenance was recognised, this is either the responsibility of the FM Contractor as per the FMA or to be renewed/replaced from the Lifecycle fund as the risk has been transferred from the DoE to the Project Company. These low Backlog Maintenance costs also evidence that the Pilot PPP Schools are being maintained in a condition consistent with that required in the Services Specification.
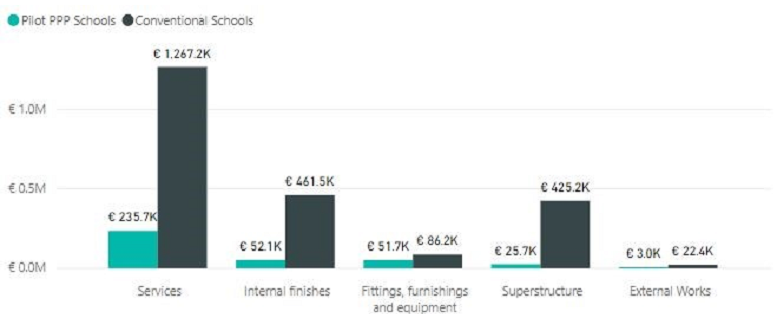
2.31 The Backlog Maintenance by group element is shown in Figure 2.11a.
Figure 2.11a - Backlog Maintenance by Group Element
2.32 The Residual Value by comparator group is shown in Figure 2.12, with the average Residual Value of the Pilot PPP Schools Bundle being €705/m2 higher than that of the Conventional Schools.
Figure 2.12 - Residual Value by Group (€/m2)

________________________________________________________________________________
4 The methodology is in line with the RICS DRC (Depreciated Replacement Cost) method of valuation for financial reporting and considers the re-build cost and Backlog Maintenance costs. This methodology is the same as that referenced in the 2004 C&AG report.