Benefits go beyond speed
The true benefits and advantages of 5G are not always well articulated. While 5G does enable ultra-high-speed data downloads, most transformative use cases for 5G are not consumer facing. Advertised speed claims will make little difference to the average mobile phone user undertaking everyday internet browsing or video streaming.
The real power of Australia's 5G network will be in delivering the greater capacity, reliability and lower latency that enable new technologies to transform Australian industries. For example:
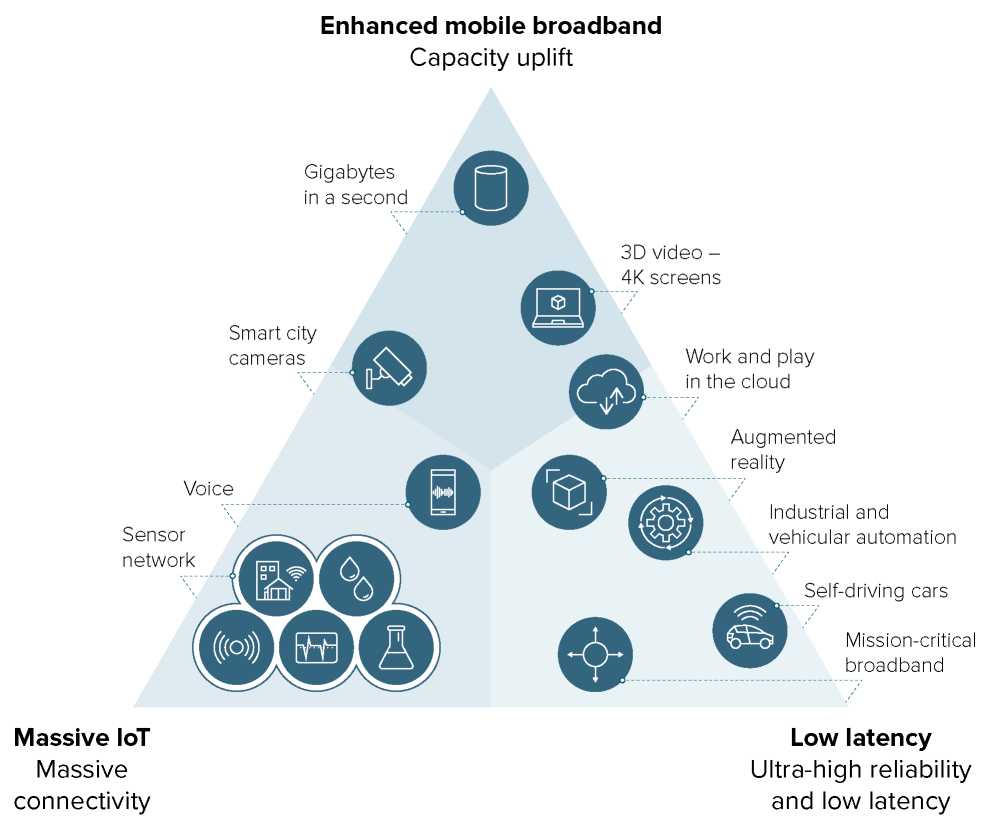
• Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB): Mobile broadband over 5G enables very large volumes of data transfer at extremely fast speeds, with data typically exchanged using mobile phones, tablets and mobile broadband connections.
• Ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC): URLLC exploits the low latency and high reliability of 5G. It supports sectors such as robotics, remote surgery, remote emergency response management, connected vehicles and augmented reality.
• Massive machine-to-machine communications (mMMC), also known as massive Machine-Type Communications: Commonly associated with the enhanced IoT, the focus of mMMC is on providing connectivity to many millions of simple narrow-bandwidth devices that infrequently send or receive small volumes of data. Common use cases include low-cost sensors, meters, actuators, trackers and wearables.
• Smart vehicles, roads and traffic management: A connected intelligent transport system allows vehicles to communicate with other vehicles, traffic signals and roadside infrastructure to share real-time, safety-related warnings. Other uses with simple data needs (such as traffic signal management) can also be enabled by 5G because of the extra reliability.
• Smart agriculture: The extensive capacity of 5G allows for the automation of tractors, livestock sensors, soil monitors and water controls. Agribusinesses are using multiple sensors and machine learning to practise precision farming, which optimises irrigation and maximises yields.
• Smart mining: 5G is creating safer, more efficient and more productive mining. The extended connectivity enables advanced Al capabilities that are providing miners with 3D visualisation, managing automated vehicles, operating robots and removing humans from potentially hazardous situations.
Establishing a nationwide 5G ecosystem
(see Figure 7.6) that supports high-impact new technologies such as the IoT is a significant economic opportunity. Modelling from 2018 shows 5G technology could yield a productivity benefit of 0.2% each year, equating to more than $50 billion in the first decade.71
With the potential to generate such a positive national economic effect, Australia needs to seize and fully enable 5G.
There was a step towards this goal in September 2020, when the Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications announced the Australian 5G Innovation Initiative. This open, competitive grants program is helping businesses to test and develop 5G uses, products and IoT applications.
While funding is important to meet Australia's 5G's aspirations, it is only part of the role that governments must play.
Figure 7.6: 5G Ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC) is a feature of the IoT ecosystem targeted at services like traffic control or remote control, which require both high reliability and low latency
Source: Qorvo (2021)72
